Trio's Rho-specific GEF domain is the missing Galpha q effector in C. elegans
- PMID: 17942708
- PMCID: PMC2045128
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1592007
Trio's Rho-specific GEF domain is the missing Galpha q effector in C. elegans
Abstract
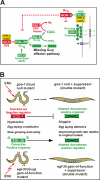
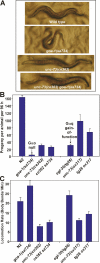
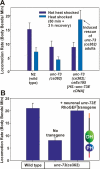
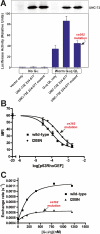
The Galpha(q) pathway is essential for animal life and is a central pathway for driving locomotion, egg laying, and growth in Caenorhabditis elegans, where it exerts its effects through EGL-8 (phospholipase Cbeta [PLCbeta]) and at least one other effector. To find the missing effector, we performed forward genetic screens to suppress the slow growth and hyperactive behaviors of mutants with an overactive Galpha(q) pathway. Four suppressor mutations disrupted the Rho-specific guanine-nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) domain of UNC-73 (Trio). The mutations produce defects in neuronal function, but not neuronal development, that cause sluggish locomotion similar to animals lacking EGL-8 (PLCbeta). Strains containing null mutations in both EGL-8 (PLCbeta) and UNC-73 (Trio RhoGEF) have strong synthetic phenotypes that phenocopy the arrested growth and near-complete paralysis of Galpha(q)-null mutants. Using cell-based and biochemical assays, we show that activated C. elegans Galpha(q) synergizes with Trio RhoGEF to activate RhoA. Activated Galpha(q) and Trio RhoGEF appear to be part of a signaling complex, because they coimmunoprecipitate when expressed together in cells. Our results show that Trio's Rho-specific GEF domain is a major Galpha(q) effector that, together with PLCbeta, mediates the Galpha(q) signaling that drives the locomotion, egg laying, and growth of the animal.
Figures





Comment in
-
Rho deep in thought.Genes Dev. 2007 Nov 1;21(21):2677-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.1615807. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17974912 Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The UNC-73/Trio RhoGEF-2 domain is required in separate isoforms for the regulation of pharynx pumping and normal neurotransmission in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2005 Sep 1;19(17):2016-29. doi: 10.1101/gad.1319905. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 16140983 Free PMC article.
-
The NCA-1 and NCA-2 Ion Channels Function Downstream of Gq and Rho To Regulate Locomotion in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2017 May;206(1):265-282. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.198820. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28325749 Free PMC article.
-
STR-33, a novel G protein-coupled receptor that regulates locomotion and egg laying in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 18;286(46):39860-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.241000. Epub 2011 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21937442 Free PMC article.
-
Rho deep in thought.Genes Dev. 2007 Nov 1;21(21):2677-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.1615807. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17974912 Review. No abstract available.
-
The GAPs, GEFs, and GDIs of heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunits.Int J Biol Sci. 2005;1(2):51-66. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.1.51. Epub 2005 Apr 1. Int J Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15951850 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired dense core vesicle maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans mutants lacking Rab2.J Cell Biol. 2009 Sep 21;186(6):881-95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200902095. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19797080 Free PMC article.
-
QuantWorm: a comprehensive software package for Caenorhabditis elegans phenotypic assays.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 8;9(1):e84830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084830. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24416295 Free PMC article.
-
Extrasynaptic acetylcholine signaling through a muscarinic receptor regulates cell migration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 5;118(1):e1904338118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1904338118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33361149 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the Neuronal Contributions of the Lipid Regulator NHR-49 Function in Lifespan and Behavior in C. elegans.Life (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;13(12):2346. doi: 10.3390/life13122346. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38137948 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Subthreshold GPCR Signals Combined by the G-Proteins Gαq and Gαs Activate the Caenorhabditis elegans Egg-Laying Muscles.J Neurosci. 2023 May 24;43(21):3789-3806. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2301-22.2023. Epub 2023 Apr 13. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37055179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes W.G., Reiter E., Violin J.D., Ren X.R., Milligan G., Lefkowitz R.J., Reiter E., Violin J.D., Ren X.R., Milligan G., Lefkowitz R.J., Violin J.D., Ren X.R., Milligan G., Lefkowitz R.J., Ren X.R., Milligan G., Lefkowitz R.J., Milligan G., Lefkowitz R.J., Lefkowitz R.J. β-Arrestin 1 and Gαq/11 coordinately activate RhoA and stress fiber formation following receptor stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:8041–8050. - PubMed
-
- Bastiani C.A., Gharib S., Simon M.I., Sternberg P.W., Gharib S., Simon M.I., Sternberg P.W., Simon M.I., Sternberg P.W., Sternberg P.W. Caenorhabditis elegans Gαq regulates egg-laying behavior via a PLCb-independent and serotonin-dependent signaling pathway and likely functions both in the nervous system and in muscle. Genetics. 2003;165:1805–1822. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bourne H.R. How receptors talk to trimeric G proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997;9:134–142. - PubMed
-
- Brundage L., Avery L., Katz A., Kim U., Mendel J.E., Sternberg P.W., Simon M.I., Avery L., Katz A., Kim U., Mendel J.E., Sternberg P.W., Simon M.I., Katz A., Kim U., Mendel J.E., Sternberg P.W., Simon M.I., Kim U., Mendel J.E., Sternberg P.W., Simon M.I., Mendel J.E., Sternberg P.W., Simon M.I., Sternberg P.W., Simon M.I., Simon M.I. Mutations in a C. elegans Gqα gene disrupt movement, egg laying, and viability. Neuron. 1996;16:999–1009. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
