Top down attentional deficits in macaques with lesions of lateral prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 17942725
- PMCID: PMC6673036
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2939-07.2007
Top down attentional deficits in macaques with lesions of lateral prefrontal cortex
Abstract
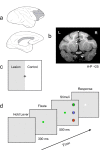
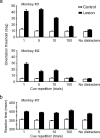
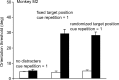
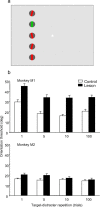
Brain imaging, electrical stimulation, and neurophysiological studies have all implicated the prefrontal cortex (PFC) in the top-down control of attention. Specifically, feedback from PFC has been proposed to bias activity in visual cortex in favor of attended stimuli over irrelevant distracters. To identify which attentional functions are critically dependent on PFC, we removed PFC unilaterally in combination with transection of the corpus callosum and anterior commissure in two macaques. In such a preparation, the ipsilesional hemisphere is deprived of top-down feedback from PFC to visual cortex, and the contralesional hemisphere can serve as an intact normal control. Monkeys were trained to fixate a central cue and discriminate the orientation of a colored target grating presented among colored distracter gratings in either the hemifield affected by the PFC lesion or the normal control hemifield. Locations of the targets and distracters were varied, and the color of the central cue specified the color of the target on each trial. The behavioral response was a bar release, and thus attentional impairments could be distinguished from impaired oculomotor control. When the cue was held constant for many trials, task performance in the affected hemifield was nearly normal. However, the monkeys were severely impaired when the cue was switched frequently across trials. The monkeys were unimpaired in a pop-out task with changing targets that did not require top-down attentional control. The PFC thus appears to play a critical role in the ability to flexibly reallocate attention on the basis of changing task demands.
Figures
References
-
- Aron AR, Monsell S, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW. A componential analysis of task-switching deficits associated with lesions of left and right frontal cortex. Brain. 2004;127:1561–1573. - PubMed
-
- Asaad WF, Rainer G, Miller EK. Neural activity in the primate prefrontal cortex during associative learning. Neuron. 1998;21:1399–1407. - PubMed
-
- Asaad WF, Rainer G, Miller EK. Task-specific neural activity in the primate prefrontal cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2000;84:451–459. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi L. The mechanism of the brain and the function of the frontal lobes. Edinburgh: Livingstone; 1922.
-
- Brass M, Ruge H, Meiran N, Rubin O, Koch I, Zysset S, Prinz W, von Cramon DY. When the same response has different meanings: recoding the response meaning in the lateral prefrontal cortex. NeuroImage. 2003;20:1026–1031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
