Interferon modulation of cellular microRNAs as an antiviral mechanism
- PMID: 17943132
- PMCID: PMC2748825
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06205
Interferon modulation of cellular microRNAs as an antiviral mechanism
Abstract
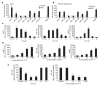
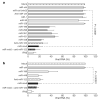
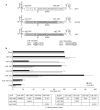
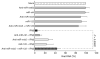
RNA interference through non-coding microRNAs (miRNAs) represents a vital component of the innate antiviral immune response in plants and invertebrate animals; however, a role for cellular miRNAs in the defence against viral infection in mammalian organisms has thus far remained elusive. Here we show that interferon beta (IFNbeta) rapidly modulates the expression of numerous cellular miRNAs, and that eight of these IFNbeta-induced miRNAs have sequence-predicted targets within the hepatitis C virus (HCV) genomic RNA. The introduction of synthetic miRNA-mimics corresponding to these IFNbeta-induced miRNAs reproduces the antiviral effects of IFNbeta on HCV replication and infection, whereas neutralization of these antiviral miRNAs with anti-miRNAs reduces the antiviral effects of IFNbeta against HCV. In addition, we demonstrate that IFNbeta treatment leads to a significant reduction in the expression of the liver-specific miR-122, an miRNA that has been previously shown to be essential for HCV replication. Therefore, our findings strongly support the notion that mammalian organisms too, through the interferon system, use cellular miRNAs to combat viral infections.
Figures
Comment in
-
Control of HCV replication: when size does not matter.Hepatology. 2008 Mar;47(3):1092-4. doi: 10.1002/hep.22267. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18302297 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cullen BR. Is RNA interference involved in intrinsic antiviral immunity in mammals? Nature Immunol. 2006;7:563–567. - PubMed
-
- Jopling CL, Yi M, Lancaster AM, Lemon SM, Sarnow P. Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific microRNA. Science. 2005;309:1577–1581. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

