Modes of administration of antibiotics for symptomatic severe urinary tract infections
- PMID: 17943784
- PMCID: PMC7003567
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003237.pub2
Modes of administration of antibiotics for symptomatic severe urinary tract infections
Abstract
Background: Urinary tract infection (UTI), worldwide, is a major source of disease in children and adults. As it may have long-term consequences such as kidney failure and hypertension, it is important to treat patients with UTI adequately. Although standard management of severe UTI usually means intravenous (IV) therapy, at least initially, there are studies showing that oral therapy may also be effective.
Objectives: To assess whether the mode of administration of antibiotic therapy for severe UTI has an effect on cure rate, reinfection rate and kidney scarring.
Search strategy: The Cochrane Renal Group's specialised register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, in The Cochrane Library), MEDLINE and EMBASE were searched. No language restriction was applied. Reference lists of relevant articles and reviews were checked for additional studies and authors of relevant articles/abstracts were contacted for further information. Date of last search: July 2007.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing different modes of antibiotic application for patients with severe UTI (children and adults) were considered.
Data collection and analysis: Study quality was assessed and data extracted. Statistical analyses were performed using the random effects model and the results expressed as relative risk (RR) for dichotomous outcomes or mean difference (WMD) for continuous data with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
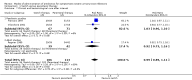
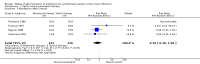
Main results: Fifteen RCTs (1743 patients) were included. Studies compared oral versus parenteral treatment (1), oral versus switch treatment (initial intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) therapy followed by oral therapy) (5), switch versus parenteral treatment (6) and single dose parenteral followed by oral therapy versus oral (1) or switch therapy (3). There was a variety of short-term and long-term outcomes, but no pooled outcomes showed significant differences. Most included studies were small though and there were few outcomes for combination in a meta-analysis.
Authors' conclusions: There is no evidence suggesting that oral antibiotic therapy is less effective for treatment of severe UTI than parenteral or initial parenteral therapy. The results of this review suggest that the mode of application does not determine therapeutic success.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures
























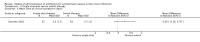




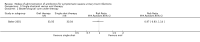


Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Baker 2001 {published data only}
-
- Baker PC, Nelson DS, Schunk JE. The addition of ceftriaxone to oral therapy does not improve outcome in febrile children with urinary tract infections. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2001;155(2):135‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Childs 1990 {published data only}
-
- Childs SJ. Intravenous and oral ciprofloxacin versus intravenous ceftazidime for the treatment of severe urinary tract infections. Diagnostic Microbiology & Infectious Disease 1990;13(2):161‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fischbach 1989 {published data only}
-
- Fischbach M, Simeoni U, Mengus L, Jehl F, Monteil H, Geisert J, et al. Urinary tract infections with tissue penetration in children: cefotaxime compared with amoxycillin/clavulanate. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1989;24 Suppl B:177‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Francois 1997 {published data only}
-
- Francois P, Bensman A, Begue P, Artaz MA, Coudeville L, Lebrun T, et al. Assessment of the efficacy and cost efficiency of two strategies in the treatment of acute pyelonephritis in children: Oral cefixime or parenteral ceftriaxone after an initial IV combination therapy. Medecine et Maladies Infectieuses 1997;27(Spec. Iss. June):667‐73. [EMBASE: 1997230388]
Gok 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gok F, Duzova A, Baskin E, Ozen S, Besbas N, Bakkaloglu A. Comparative study of cefixime alone versus intramuscular ceftizoxime followed by cefixime in the treatment of urinary tract infections in children. Journal of Chemotherapy 2001;13(3):277‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hoberman 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hoberman A, Wald ER, Hickey RW, Baskin M, Charron M, Majd M, et al. Oral versus initial intravenous therapy for urinary tract infections in young febrile children. Pediatrics 1999;104(1 Pt 1):79‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Millar 1995 {published data only}
-
- Millar LK, Wing DA, Paul RH, Grimes DA. Outpatient treatment of pyelonephritis in pregnancy: A randomized controlled trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1995;86(4 Pt 1):560‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mombelli 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mombelli G, Pezzoli R, Pinoja‐Lutz G, Monotti R, Marone C, Franciolli M. Oral vs intravenous ciprofloxacin in the initial empirical management of severe pyelonephritis or complicated urinary tract infections: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 1999;159(1):53‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Montini 2007 {published data only}
-
- Montini G, Murer L, Gobber D, Comacchio S, Toffolo A, Dall'Amico R, et al. Oral vs inital intravenous antibiotic treatment of urinary tract infections in children: a multicentre study [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):816. [CENTRAL: CN‐00446817]
Neuhaus 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Buechner K, Girardin F, Berger C, Willi U, Nadaf D, Neuhaus T for the Swiss Pyelonephritis Study Group. Randomised controlled trial of oral versus sequential intravenous/oral cephalosporins in DMSA scintigraphy‐documented acute pyelonephritis [abstract no: COD. OP 18]. Pediatric Nephrology 2006;21(10):1511.
-
- Neuhaus TJ, Büchner K, Girardin E, Willi U, Berger C, Nadal D. Oral verus sequentiel intravenous/oral cephalosporin‐therapy in DMSA‐scintigraphy documented acute pyelonephritis: randomized Swiss pyelonephritis‐study [abstract] [Orale versus sequentiell intravenös/orale Cephalosporin‐Therapie bei DMSA‐Szintigraphie dokumentierter akuter Pyelonephritis: Randomisierte Schweizer Pyelonephritis‐Studie]. Nieren‐ und Hochdruckkrankheiten 2007;36(2):43.
Noorbakhsh 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Noorbakhsh S, Lari AR, Masjedian F, Mostafavi H, Alaghehbandan R. Comparison of intravenous aminoglycoside therapy with switch therapy to cefixime in urinary tract infections. Saudi Medical Journal 2004;25(10):1513‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Puppo 1989 {published data only}
-
- Puppo P, Germinale F, Rose A. Aztreonam vs norfloxacin: a comparative study of the treatment of urinary tract infections in ambulatory and hospitalized patients. Clinica Terapeutica 1989;129(2):113‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Regnier 1989 {published data only}
-
- Regnier B, Brion N, Calamy G, Dureux JB, Humbert G, Imbert Y, et al. A comparative study of intra‐venous ceftriaxone followed by oral cefixime versus parenteral ceftriaxone alone in the treatment of severe upper urinary tract infections. Presse Medicale 1989;18(32):1617‐21. [EMBASE: 1989252114] - PubMed
Sanchez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sanchez M, Collvinent B, Miro O, Horcajada JP, Moreno A, Marco F, et al. Short‐term effectiveness of ceftriaxone single dose in the initial treatment of acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis in women. A randomised controlled trial. Emergency Medicine Journal 2002;19(1):19‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Vilaichone 2001 {published data only}
-
- Vilaichone A, Watana D, Chaiwatanarat T. Oral ceftibuten switch therapy for acute pyelonephritis in children. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2001;84 Suppl 1:S61‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abraham 1982 {published data only}
-
- Abraham E, Baraff LJ. Oral versus parenteral therapy of pyelonephritis. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical & Experimental 1982;31(4):536‐43. [EMBASE: 1982138442]
Ahmetagic 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ahmetagic S, Jusufovic E, Cengic D, Koluder N, Bajramovic N, Calkic L, et al. Clinical study of the efficacy of the antimicrobiotic agent amoxicillin + clavunalic acid (xiclav) and the possibility of early parenteral to oral switch therapy in the management of Infections. Medicinski Arhiv 2003;57(5‐6):263‐6. - PubMed
Angel 1990 {published data only}
-
- Angel JL, O'Brien WF, Finan MA, Morales WJ, Lake M, Knuppel RA. Acute pyelonephritis in pregnancy: a prospective study of oral versus intravenous antibiotic therapy. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1990;76(1):28‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Benador 2001 {published data only}
Buchi 1988 {published data only}
-
- Buchi W, Casey PA. Experience with parenteral and sequential parenteral‐oral amoxicillin/clavulanate (augmentin) in hospitalized patients. Infection 1988;16(5):306‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bunnag 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bunnag T, Kietkajornkul C. Out‐patient antibiotics switch therapy in pediatric urinary tract infection. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2003;86 Suppl 3:543‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cherubin 1986 {published data only}
-
- Cherubin C, Stilwell S. Norfloxacin versus parenteral therapy in the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections and resistant organisms. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases Supplement 1986;48:32‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Concia 2006 {published data only}
-
- Concia E, Marchetti F, LEVT07 Study Group. Early discharge of hospitalised patients with community‐acquired urosepsis when treated with levofloxacin in sequential therapy. Archivio Italiano di Urologia, Andrologia 2006;78(3):112‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cox 1987 {published data only}
-
- Cox CE, McCabe RE, Grad C. Oral norfloxacin versus parenteral treatment of nosocomial urinary tract infection. American Journal of Medicine 1987;82(6B):59‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Scheife RT, Cox CE, McCabe RE, Grad C. Norfloxacin vs best parenteral therapy in treatment of moderate to serious, multiply‐resistant, nosocomial urinary tract infections: a pharmacoeconomic analysis. Urology 1988;32(3 Suppl):24‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cox 1989 {published data only}
-
- Cox CE. Brief report: Sequential intravenous and oral ciprofloxacin versus intravenous ceftazidime in the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. American Journal of Medicine 1989;87(5A):157S‐159S. [EMBASE: 1990005329] - PubMed
Daly 1989 {published data only}
-
- Daly JS, Worthington MG, Razvi SA, Robillard R. Brief report: Intravenous and sequential intravenous and oral ciprofloxacin in the treatment of severe infections. American Journal of Medicine 1989;87(5A):232S‐234S. [EMBASE: 1990005347] - PubMed
Esposito 1991 {published data only}
-
- Esposito S, Sardaro C, Gaeta GB, Galante D, Giusti G, Basani F. Cefodizime (HR221) versus norfloxacin for treatment of urinary tract infections. Journal of Chemotherapy 1991;31(1):42‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fang 1991 {published data only}
-
- Fang G, Brennen C, Wagener M, Swanson D, Hilf M, Zadecky L, et al. Use of ciprofloxacin versus use of aminoglycosides for therapy of complicated urinary tract infection: Prospective, randomized clinical and pharmacokinetic study. Antimicrobial Agents & Chemotherapy 1991;35(9):1849‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Fass 1989 {published data only}
-
- Fass RJ, Plouffe JF, Russell JA. Intravenous/oral ciprofloxacin versus ceftazidime in the treatment of serious infections. American Journal of Medicine 1989;87(5A):164S‐168S. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gangji 1989 {published data only}
-
- Gangji D, Jacobs F, Jonckheer J, Coppens L, Serruys E, Hanotte F, et al. Brief report: Randomized study of intravenous versus sequential intravenous/oral regimen of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of gram‐negative septicemia. American Journal of Medicine 1989;87(5A):206S‐208S. [EMBASE: 1990005341] - PubMed
Gaut 1989 {published data only}
-
- Gaut PL, Carbon WC, Ching WTW, Meyer RD. Intravenous/oral ciprofloxacin therapy versus intravenous ceftazidime therapy for selected bacterial infections. American Journal of Medicine 1989;78(5A):169S‐175S. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gelfand 1993 {published data only}
-
- Gelfand MS, Simmons BP, Craft RB, Grogan J. A sequential study of intravenous and oral fleroxacin in the treatment of complicated urinary tract infection. American Journal of Medicine 1993;94(3A):126S‐130S. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Giamarellou 1989 {published data only}
Harding 1993 {published data only}
-
- Harding G, Nicolle L, Wenman W, Richards G, Louie T, Martel A, et al. Randomised comparison of oral ciprofloxacin vs standard parenteral therapy in the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Drugs 1993;46(Suppl 3):333‐4. [EMBASE: 1993243049]
Kalager 1992 {published data only}
-
- Kalager T, Andersen BM, Bergan T, Brubakk O, Bruun JN, Doskeland B, et al. Ciprofloxacin versus a tobramycin/cefuroxime combination in the treatment of serious systemic infections: A prospective, randomized and controlled study of efficacy and safety. [erratum appears in Scand J Infect Dis 1993;25(2):271]. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1993;24(5):637‐46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kanellakopoulou 1990 {published data only}
-
- Kanellakopoulou K, Giamarellou H. Clinical experinece with parenteral and oral ofloxacin in severe infections. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases Supplement 1990;22(68):64‐9. [EMBASE: 1990265153] - PubMed
Le Conte 2001 {published data only}
-
- Conte P, Simon N, Bourrier P, Merit JB, Lebrin P, Bonnieux J, et al. Acute pyelonephritis. Randomized multicenter double‐blind study comparing ciprofloxacin with combined ciprofloxacin and tobramycin. Presse Medicale 2001;30(1):11‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Levtchenko 2001a {published data only}
-
- Levtchenko E, Lahy C, Levy J, Ham H, Piepsz A. Treatment of children with acute pyelonephritis: a prospective randomized study. Pediatric Nephrology 2001;16(11):878‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lorian 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lorian V, Pavletich K. Oral ciprofloxacin versus intravenous therapy with other non‐quinolone agents: A study of 291 infections. Drugs Under Experimental & Clinical Research 1994;20(5):209‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Matilla 1982 {published data only}
-
- Matilla J, Kyronseppa H, Pettersson T, et al. Parenteral cephalexin lysinate followed by oral cephalexin in the treatment of serious pulmonary and urinary tract infections ‐ a comparison with cephradine. Drugs Under Experimental & Clinical Research 1982;8(5):493‐8. [EMBASE: 1983059737]
Michaelis 1993 {published data only}
-
- Michaelis WE, Bischoff W, Braun HP, Bruehl P, Gerhardts W, Hochberg K, et al. Combined intravenous and oral treatment in complicated UTI: Lomefloxacin vs ciprofloxacin [abstract]. Drugs 1993;46(Suppl 3):348. [EMBASE: 1993243057]
Nicolle 1991 {published data only}
-
- Nicolle LE, Degelau J, Alessi P, Cullison J, Meyers B. Ofloxacin use in a geriatric population. Chemotherapy 1991;37 Suppl 1:49‐51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Paladino 1991 {published data only}
-
- Paladino JA, Sperry HE, Backes JM, Gelber JA, Serrianne DJ, Cumbo TJ, et al. Clinical and economic evaluation of oral ciprofloxacin after an abbreviated course of intravenous antibiotics. American Journal of Medicine 1991;91(5):462‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Peacock 1989 {published data only}
-
- Peacock Jr JE, Pegram PS, Weber SF, Leone PA. Prospective, randomized comparison of sequential intravenous followed by oral ciprofloxacin with intravenous ceftazidime in the treatment of serious infections. American Journal of Medicine 1989;87(5A):185S‐190S. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Raz 1988 {published data only}
-
- Raz R, Chaimowitsh G, Keness Y, Sudarsky M. Oral ciprofloxacin as a follow‐up treatment for complicated urinary tract infections due to organisms resistant to oral antibiotics. Urologia 1988;55(2):123‐7. [EMBASE: 1988159373]
Robson 1993 {published data only}
-
- Robson RA, Bailey RR, Lynn KL. Lomefloxacin pharmacokinetics after intravenous and oral administration in patients with acute pyelonephritis [abstract]. Drugs 1993;46(Suppl 3):269. [EMBASE: 1993243011]
Safrin 1988 {published data only}
-
- Safrin S, Siegel D, Black D. Pyelonephritis in adult women: Inpatient versus outpatient therapy. American Journal of Medicine 1988;85(6):793‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sannier 2000 {published data only}
-
- Sannier N, Masne A, Sayegh N, Gaillard JL, Cheron G. Ambulatory management of acute pyelonephritis in children. Acta Paediatrica 2000;89(3):372‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Timmerman 1992 {published data only}
-
- Timmerman C, Hoepelman I, Hond J, Boon T, Schreinemachers L, Mensink H, et al. Open, randomized comparison of pefloxacin and cefotaxime in the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Infection 1992;20(1):34‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
Dickersin 1994
Gonzalez 1999
-
- Gonzalez CM, Schaeffer AJ. Treatment of urinary tract infection: what's old, what's new, and what works. World Journal of Urology 1999;17(6):372‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hansson 1999
-
- Hansson S, Jodal U. Urinary tract infection. In: Barratt TM, Avner ED, HarmanWE editor(s). Pediatric Nephrology. 4th Edition. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999:835‐50.
Higgins 2003
Jones 1996
Kunin 1994
-
- Kunin CM. Urinary tract infections in females. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1994;18(1):1‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lefebvre 1996
-
- Lefebvre C, McDonald S. Development of a sensitive search strategy for reports of randomized controlled trials in EMBASE. Fourth International Cochrane Colloquium; 1996 Oct 20‐24; Adelaide (Australia). 1996.
Levtchenko 2001
-
- Levtchenko E, Ham HR, Levy J, Piepsz A. Attitude of Belgian pediatricians toward strategy in acute pyelonephritis. Pedatric Nephrology 2001;16(2):113‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Master List 2007
-
- United States Cochrane Center. Master list of journals being searched. http://apps1.jhsph.edu/cochrane/masterlist.asp (accessed 2007).
McCracken 1989
-
- McCracken GH Jr. Options in antimicrobial management of urinary tract infections in infants and children. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1989;8(8):552‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Orenstein 1999
-
- Orenstein R, Wong ES. Urinary tract infections in adults. American Family Physician 1999;59(5):1225‐34, 1237. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ransley 1981
-
- Ransley PG, Risdon RA. Reflux nephropathy: effects of antimicrobial therapy on the evolution of the early pyelonephritic scar. Kidney International 1981;20(6):733‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Smellie 1994
Stamm 1993
-
- Stamm WE, Hooton TM. Management of urinary tract infections in adults. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;329(18):1328‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Winberg 1974
-
- Winberg J, Andersen HJ, Bergstrom T, Jacobsson B, Larson H, Lincoln K. Epidemiology of symptomatic urinary tract infection in childhood. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica ‐ Supplement 1974, (252):1‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

