Topical pimecrolimus for eczema
- PMID: 17943859
- PMCID: PMC10043871
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005500.pub2
Topical pimecrolimus for eczema
Abstract
Background: Pimecrolimus was developed as an alternative to topical corticosteroids for treating eczema (atopic dermatitis) but its efficacy and safety compared with existing treatments remains unclear.
Objectives: To assess the effects of topical pimecrolimus for treating eczema.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Skin Group Specialised Register (to October 2006), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library Issue 3, 2006), MEDLINE (from 2003 to October 2006), and EMBASE (from 2005 to October 2006). We also contacted researchers and manufacturers in the field.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials of 1.0% topical pimecrolimus used twice daily compared against other topical comparators for treating eczema.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently examined each retrieved study for eligibility and extracted data for efficacy, tolerability and safety. A random-effects model was used to estimate the pooled risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).
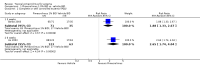
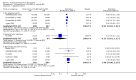
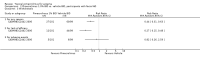
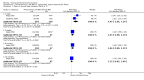
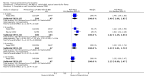
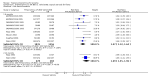
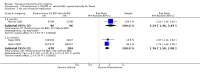
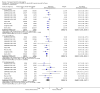
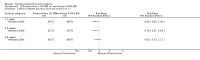
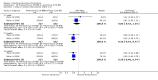
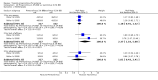
Main results: We included 31 trials (8019 participants) in the analysis. In short-term (</= 6 weeks) trials, pimecrolimus cream was significantly more effective and well-tolerated than vehicle (cream base, but not containing pimecrolimus). In long-term trials (>/=6 months), pimecrolimus was significantly better than vehicle in preventing flares (9 trials, 3091 participants, RR 1.47, 95% CI 1.32 to 1.64 at six months) and in improving quality of life. Pimecrolimus was significantly less effective than two topical corticosteroids, i.e. 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide for investigators' global assessment (1 trial, 658 participants, RR 0.75, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.83) and 0.1% betamethasone valerate for participants' global assessment (1 trial, 87 participants, RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.45 to 0.81) at three weeks. Pimecrolimus was also associated with significantly more overall withdrawals and skin burning. None of the trials reported on key adverse effects such as thinning of skin. Pimecrolimus was significantly less effective than 0.1% tacrolimus for investigators' global assessment at six weeks (RR 0.58, 95% CI 0.46 to 0.74) and led to more withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 2.37, 95% CI 1.10 to 5.08) based on two trials involving 639 participants, but there was no significant difference in proportions of participants experiencing any adverse events.
Authors' conclusions: Topical pimecrolimus is less effective than moderate and potent corticosteroids and 0.1% tacrolimus. The therapeutic role of topical pimecrolimus is uncertain due to the absence of key comparisons with mild corticosteroids.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures





































Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
ASM981C2315 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol ASM981C2315). A 26‐week, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the incidence of atopic dermatitis flares when pimecrolimus cream 1% is used at the first signs and/or symptoms of atopic dermatitis and its safety and tolerability in children and adolescents 2‐17 years of age. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
ASM981C2316 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol ASM981C2316). A 26‐week, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the incidence of atopic dermatitis flares when pimecrolimus cream 1% is used at the first signs and/or symptoms of atopic dermatitis and its safety and tolerability in adults 18 years of age and older. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
ASM981C2402 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol ASM981C2402). An exploratory, randomized, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled, multicenter, parallel dose study investigating the use of pimecrolimus cream 1% in mild to moderate atopic dermatitis patients who demonstrate a clinical insensitivity to topical glucocorticoids. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
ASM981CDE10 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol ASM981CDE10). A 24‐week, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study on pimecrolimus cream 1% assessing the steroid‐sparing effect in the long term management of pediatric patients with severe atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
Barba 2003 {published data only}
-
- Barba JF, Beirana A, Cohen V, Dominguez L, Duran C, Leon G, et al. Pimecrolimus cream 1% is effective, well tolerated and safe in infants and children with atopic eczema of the face. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 2003; Vol. 17, issue Suppl 3:P2.35.
CASM981C1301 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis CASM981C1301 Norvatis (protocol CASM981C1301) Norvatis CASM981C1301. Confirmatory study in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis‐ multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group, vehicle‐controlled study with a 26‐weeks treatment phase to determine the efficacy, safety of pimecrolimus cream for long‐term treatment of pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C1303 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C1303). Confirmatory study in adult patients with atopic dermatitis‐ multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group, vehicle‐controlled study with a 26‐week treatment phase to determine the efficacy, safety of pimecrolimus cream for long‐term treatment of adult patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2314 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2314). A 22‐week randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind study to compare a pimecrolimus cream 1% twice daily (BID) maintenance dosing regimen to a once daily (OD) maintenance dosing regimen in the management of atopic dermatitis in pediatric subjects. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 31th October 2006) 2006.
CASM981C2322 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2322). A 4‐week, randomized, multicenter, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled, parallel‐group clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in the short‐term treatment of patients with mild to moderate Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema). www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2436 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2436). A multicenter, 5‐week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled, parallel group study exploring the effects of pimecrolimus cream 1% (twice daily application) vs. placebo control (twice daily application) on the molecular and cellular profile of adult male patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
CASM981C2442 2006 {published data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2442). A 12 week multicenter study consisting of a 6 week double blind, randomized, vehicle controlled, parallel group phase, followed by a 6 week open label phase, to assess the safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus cream 1% in mild to moderate head and neck atopic dermatitis of patients intolerant of topical corticosteroid. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 31th October 2006) 2006.
CASM981CUS03 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CUS03). A 6‐month, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus 1% cream twice daily vs. standard of care in the management of mild to severe atopic dermatitis in adults. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
Eichenfield (a) 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, Langley RG, Cherill R, Marshall K, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (http://www.fda.gov/cder/approval/index.htm) 2002 (accessed 1st November 2003);46(4):495‐504. - PubMed
Eichenfield (b) 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, Langley RG, Cherill R, Marshall K, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (http://www.fda.gov/cder/approval/index.htm) 2002 (accessed 1st November 2003);46(4):495‐504. - PubMed
Ho 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ho VC, Gupta A, Kaufmann R, Todd G, Vanaclocha F, Takaoka R, Folster‐Holst R, Potter P, Marshall K, et al. Safety and efficacy of nonsteroid pimecrolimus cream 1% in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2003;142(2):155‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kapp 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kapp A, Papp K, Bingham A, Folster‐Holst R, Ortonne JP, Potter PC, Gulliver W, Paul C, Molloy S, Barbier N, Thurston M, Prost Y, Flare Reduction in Eczema with Elidel (infants) multicenter investigator study group. Long‐term management of atopic dermatitis in infants with topical pimecrolimus, a nonsteroid anti‐inflammatory drug. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2002;110(2):277‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kaufmann 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kaufmann R, Bieber T, Helgesen AL, Andersen BL, Luger T, Poulin Y, et al. Onset of pruritus relief with pimecrolimus cream 1% in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: a randomized trial. Allergy 2006;61(3):375‐81. - PubMed
Kempers 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kempers S, Boguniewicz M, Carter E, Jarrat M, Pariser D, Stewart D. Comparison of pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% in paediatric patients with atopic eczema. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2003;17:41.
-
- Kempers S, Boguniewicz M, Carter E, Jarratt M, Pariser D, Stewart D, et al. A randomized investigator‐blinded study comparing pimecrolimus cream 1% with tacrolimus ointment 0.03% in the treatment of pediatric patients with moderate atopic dermatitis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2004;51(4):515‐25. - PubMed
Leo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Leo HL, Bender BG, Leung SB, Tran ZV, Leung DY. Effect of pimecrolimus cream 1% on skin condition and sleep disturbance in children with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2004;114(3):691‐93. - PubMed
Ling 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ling M, Gottlieb A, Pariser D, Caro I, Stewart D, Scott G, et al. A randomized study of the safety, absorption and efficacy of pimecrolimus cream 1% applied twice or four times daily in patients with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2005;16(3):142‐8. - PubMed
-
- Ling M, Gottlieb AB, Abrams K. Ling M, Gottlieb AB, Abrams K. Pimecrolimus cream 1%; bid and qid application were equally effective and well tolerated. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2002; Vol. 16:27.
Luger 2001 {published data only}
-
- Luger T, Leent EJM, Graeber M, Hedgecock S, Thurston M, Kandra A, et al. SDZ ASM 981: An emerging safe and effective treatment for atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 2001;144(4):788‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Luger 2004 {published data only}
-
- Luger TA, Lahfa M, Folster‐Holst R, Gulliver WP, Allen R, Molloy S, et al. Long‐term safety and tolerability of pimecrolimus cream 1% and topical corticosteroids in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2004;15(3):169‐78. - PubMed
Meurer 2002 {published data only}
-
- Meurer M, Folster‐Holst R, Wozel G, Weidinger G, Junger M, Brautigam M, et al. Pimecrolimus cream in the long‐term management of atopic dermatitis in adults: a six‐month study. Dermatology 2002;205(3):271‐77. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Paller (a) 2005 {published data only}
-
- Paller AS, Lebwohl M, Fleischer AB Jr, Antaya R, Langley RG, Kirsner RS, et al. Tacrolimus ointment is more effective than pimecrolimus cream with a similar safety profile in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 3 randomized, comparative studies. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(5):810‐22. - PubMed
Paller (b) 2005 {published data only}
-
- Paller AS, Lebwohl M, Fleischer AB Jr, Antaya R, Langley RG, Kirsner RS, et al. Tacrolimus ointment is more effective than pimecrolimus cream with a similar safety profile in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 3 randomized, comparative studies. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(5):810‐22. - PubMed
Paller (c) 2005 {published data only}
-
- Paller AS, Lebwohl M, Fleischer AB Jr, Antaya R, Langley RG, Kirsner RS, et al. Tacrolimus ointment is more effective than pimecrolimus cream with a similar safety profile in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 3 randomized, comparative studies. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(5):810‐22. - PubMed
Siegfried 2006 {published data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CUS04). A 6‐month, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1 % twice daily vs. standard of care in the management of mild to severe atopic dermatitis in children 3 months to 11 years. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
-
- Siegfried E, Korman N, Molina C, Kianifard F, Abrams K. Safety and efficacy of early intervention with pimecrolimus cream 1% combined with corticosteroids for major flares in infants and children with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2006;17(3):143‐50. - PubMed
Staab 2005 {published data only}
-
- Staab D, Kaufmann R, Brautigam M, Wahn U. Treatment of infants with atopic eczema with pimecrolimus cream 1% improves parents' quality of life: a multicenter, randomized trial. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2005;16(6):527‐33. - PubMed
Thaci 2003 {published data only}
-
- Thaci D, Folster‐Holst R, Hoger P, Kaufmann R, Brautigam M, Weidinger G, et al. Pimecrolimus cream 1% is effective in the treatment of atopic eczema in infants irrespective of clinical score. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 2003; Vol. 17, issue Suppl 3:P2.37.
Wahn 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wahn U, Bos JD, Goodfield M, Caputo R, Papp K, Manjra A, et al. Flare Reduction in Eczema with Elidel (Children) Multicenter Investigator Study Group. Efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream in the long‐term management of atopic dermatitis in children. Pediatrics 2002;110(1:Pt 1):e2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Whalley 2002 {published data only}
-
- Whalley D, Huels J, McKenna S P, Assche D. The benefit of pimecrolimus (Elidel, SDZ ASM 981) on parents' quality of life in the treatment of pediatric atopic dermatitis. Pediatrics 2002;110(6):1133‐6. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ball 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ball C, Mason T. A double‐blind, randomized, parallel‐group, multi‐center study to compare 1% SDZ ASM 981 cream and vehicle in their ability to maintain remission of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in adults, for up to one year (Novartis protocol CASM981GB01). Novartis Clinical Study Report 2002.
Belsito 2004 {published data only}
-
- Belsito DV, Fowler JF Jr, Marks JG Jr, Pariser DM, Hanifin J, Duarte IA, et al. Pimecrolimus cream 1%: a potential new treatment for chronic hand dermatitis. Cutis 2004;73(1):31‐8. - PubMed
CASM9819315E1 2005 {published data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM9810315E1). A 12‐month open‐label noncontrolled extension to a randomized, multicenter parallel group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in the long‐term management of atopic dermatitis in children from 3 months to 23 months of age. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C1302 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C1302). Extension study following confirmatory study in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
CASM981C1304 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C1304). Extension study following confirmatory study in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
CASM981C2405 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2405). A 6‐month open‐label, multinational, effectiveness, and safety study of pimecrolimus cream 1% in subjects with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2405‐ext.200 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2405‐ext). A open‐label effectiveness and safety study of pimecrolimus cream 1% in subjects with atopic dermatitis (AD) who completed study CASM981C2405. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2420 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2420). Naturalistic, open‐label, multicenter study of long‐term management in patients = 3 months of age with mild or moderate atopic dermatitis using pimecrolimus cream 1%. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2421 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CAS981C2421). A double‐blind, randomized, intra–patient comparison of Pimecrolimus 1% Cream vs. placebo in the treatment of vitiligo.. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2434 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2434). A randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the time to onset of pruritus improvement during the first week of Pimecrolimus cream 1% treatment in adult patients (=18 years old) with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2434E1 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2434E1). A 5‐week open label, multicenter, non‐comparative extension study in patients (>= 18 years old) with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis to provide patients who completed the core study, CASM981C2434, access to pimecrolimus cream 1% treatment. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CEG01 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CEG01). A multicentre, single‐arm prospective, open‐label study to assess the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in patients with atopic dermatitis in daily practice settings. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CES01 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CES01). A 6‐month randomized multi‐center vehicle‐controlled parallel‐group study of 3 double‐blind weeks followed by a 23‐week open‐label phase to study the safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus cream 1% in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis on the face. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CJP01 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (CASM981CJP01). Assessment of blood concentrations, tolerability, and efficacy of pimecrolimus cream 1% in Japanese pediatric patients. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CPI01 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CPI01). Naturalistic, open‐label, multicenter study of short‐term management in early school‐aged (6‐10 years old) children with mild or moderate atopic dermatitis using pimecrolimus cream 1%. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CUS05 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CUS05). An 8‐week randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled multicenter study in adults to assess the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus 1% cream twice daily in the treatment of inverse psoriasis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CUS08 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CUS08). A randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the time of pruritus improvement during the first week of pimecrolimus cream 1% treatment in patients =2 years old with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CZA01 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CZA01). A 3‐month open label, national, quality of life , and safety study with pimecrolimus cream, 1% in children (age 2‐12 years ) with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
CASM981DE06 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981DE06). A single‐center, randomized, double‐blind, intraindividual, experimental vehicle‐controlled investigation of the protective effect of Pimecolimus cream 1% on the development of atopic eczema by the atopy patch test (APT). www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981M2301 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- Novartis (protocol CASM981M2301). A 6‐week randomized, multicenter, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel group study to investigate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in patients with mild to moderate chronic hand dermatitis, followed by a 6‐week open‐label phase to assess the safety of pimecrolimus cream 1%. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?... (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
McKenna 2006 {published data only}
-
- McKenna SP, Whalley D, Prost Y, Staab D, Huels J, Paul CF, et al. Treatment of paediatric atopic dermatitis with pimecrolimus (Elidel, SDZ ASM 981): impact on quality of life and health‐related quality of life. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2006;20(3):248‐54. - PubMed
Meads 2005 {published data only}
-
- Meads DM, McKenna SP, Kahler K. The quality of life of parents of children with atopic dermatitis: interpretation of PIQoL‐AD scores. Quality of Life Research 2005;14(10):2235‐45. - PubMed
Meurer 2004 {published data only}
-
- Meurer M, Fartasch M, Albrecht G, Vogt T, Worm M, Ruzicka T, et al. Long‐term efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in adults with moderate atopic dermatitis. Dermatology 2004;208(4):365‐72. - PubMed
Papp 2004 {published data only}
-
- Papp K, Staab D, Harper J, Potter P, Puig L, Ortonne JP, et al. Effect of pimecrolimus cream 1% on the long‐term course of pediatric atopic dermatitis. International Journal of Dermatology 2004;43(12):978‐83. - PubMed
Papp 2005 {published data only}
-
- Papp KA, Werfel T, Folster‐Holst R, Ortonne JP, Potter PC, Prost Y, et al. Long‐term control of atopic dermatitis with pimecrolimus cream 1% in infants and young children: a two‐year study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(2):240‐6. - PubMed
Queille‐Roussel 2001 {published data only}
-
- Queille‐Roussel C, Paul C, Duteil L, Lefebvre MC, Rapatz G, Zagula M, et al. The new topical ascomycin derivative SDZ ASM 981 does not induce skin atrophy when applied to normal skin for 4 weeks: a randomized, double‐blind controlled study. British Journal of Dermatology 2001;144(3):507‐13. - PubMed
Rappersberger 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rappersberger K, Komar M, Ebelin ME, Scott G, Burtin P, Greig G, et al. Pimecrolimus identifies a common genomic anti‐inflammatory profile, is clinically highly effective in psoriasis and is well tolerated. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2002;119(4):876‐87. - PubMed
Van Leent 1998 {published data only}
-
- Leent EJ, Graber M, Thurston M, Wagenaar A, Spuls PI, Bos JD. Effectiveness of the ascomycin macrolactam SDZ ASM 981 in the topical treatment of atopic dermatitis. Archives of Dermatology 1998;134(7):805‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Weissenbacher 2006 {published data only}
-
- Weissenbacher S, Traidl‐Hoffmann C, Eyerich K, Katzer K, Braeutigam M, Loeffler H, et al. Modulation of atopy patch test and skin prick test by pretreatment with 1% pimecrolimus cream. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 2006;140(3):239‐44. - PubMed
Wolff 2005 {published data only}
-
- Wolff K, Fleming C, Hanifin J, Papp K, Reitamo S, Rustin M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of three different doses of oral pimecrolimus in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized controlled trial. British Journal of Dermatology 2005;152(6):1296‐1303. - PubMed
Additional references
Arellano 2006
-
- Arellano FM, Wentworth CE, Arana A, Fernandez C, Paul CF. Risk of Lymphoma Following Exposure to Calcineurin Inhibitors and Topical Steroids in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2006; Vol. advance online publication, 9 November 2006. - PubMed
Beattie 2003
-
- Beattie PE, Lewis‐Jones MS. Parental knowledge of topical therapies in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 2003;28:549‐53. - PubMed
Charman (a) 2000
-
- Charman C, Williams H. Outcome measures of disease severity in atopic eczema. Archives of Dermatology 2002;136(6):763‐9. - PubMed
Charman (b) 2000
-
- Charman CR, Morris AD, Williams HC. Topical corticosteroid phobia in patients with atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 2000;142:931‐6. - PubMed
Charman 2003
-
- Charman C, Chambers C, Williams H. Measuring atopic dermatitis severity in randomized controlled clinical trials: what exactly are we measuring?. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2003;120(6):932‐41. - PubMed
Cookson 2002
-
- Cookson W. Genetics and genomics of asthma and allergic diseases. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2002;113(5):832‐6.
Deeks 2001
-
- Deeks JJ, Altman DG, Bradburn MJ. Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combing results form several studies in meta‐analysis. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic reviews in health care: meta‐analysis in context. London: BMJ Publishing Group, 2001:385‐12. [072791488X]
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Ellis 2002
-
- Ellis CN, Drake LA, Prendergast MM, Abramovits W, Boguniewicz M, Daniel CR, et al. Cost of atopic dermatitis and eczema in the United States. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2002;46(3):361‐70. - PubMed
Ellis 2003
-
- Ellis C, Luger T, on behalf of the ICCAD II Faculty. International Consensus Conference on Atopic Dermatitis II (ICCAD II): clinical update and current treatment strategies. British Journal of Dermatology 2003;148(Suppl. 63):3‐10. - PubMed
EMEA 2006
-
- European Agency for the Evaluation of Medical Products. Questions and answers on Protopic/Protopy and Elidel. http://www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/general/direct/pr/8027006en.pdf (accessed 31th March 2006) 2006.
Emerson 1998
-
- Emerson RM, Williams HC, Allen BR. Severity distribution of atopic dermatitis in the community and its relationship to secondary referrals. British Journal of Dermatology 1998;139:73‐6. - PubMed
Emerson 2001
-
- Emerson RM, Williams HC, Allen BR. What is the cost of atopic dermatitis in preschool children?. British Journal of Dermatology 2001;143:514‐22. - PubMed
FDA 2005
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. FDA Public Health Advisory: Elidel (pimecrolimus) Cream and Protopic (tacrolimus) Ointment. http://www.fda.gov/cder/drug/advisory/elidel_protopic.htm (Accessed 4th January 2007) 2005.
FDA 2006
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Alert for Healthcare Professionals: Pimecrolimus (marketed as Elidel). http://www.fda.gov/cder/drug/InfoSheets/HCP/ElidelHCP.pdf (accessed 1st July 2006) 2006.
Flohr 2004
-
- Flohr C, Johansson SG, Wahlgren CF, Williams H. How atopic is atopic dermatitis?. Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2004;114(1):150‐8. - PubMed
Freeman 2006
-
- Freeman SR, Williams HC, Dellavalle RP. The increasing importance of systematic reviews in clinical dermatology research and publication. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2006;126(111):2357‐60. - PubMed
Gieler 1999
-
- Gieler U, Hohmann M, Niemeler V, Kupfer J. Cost evaluation of atopic eczema. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 1999;10:S15‐20.
Hanifin 1980
-
- Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic eczema. Acta Dermato Venerologica (Stockholm) 1980;92:44‐7.
Herd 2000
-
- Herd RM. The morbidity and cost of atopic dermatitis. In: Williams HC editor(s). Atopic dermatitis. Vol. 85‐95, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
Higgins 2003
Hoare 2000
Johansson 2004
-
- Johansson SG, Bieber T, Dahl R, Friedmann PS, Lanier BQ, Lockey RF, et al. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2004;113(5):832‐6. - PubMed
Juni 2001
Kay 1994
-
- Kay J, Gawkroger DJ, Mortimer MJ, Jaron AG. The prevalence of childhood atopic eczema in a general population. Journal of American Academy of Dermatology 1994;30:35‐9. - PubMed
Kiebert 2002
-
- Kiebert G, Sorensen SV, Revicki D, Fagan SC, Doyle JJ, Cohen J, et al. Atopic dermatitis is associated with a decrement in health‐related quality of life. International Journal of Dermatology 2002;41:151‐8. - PubMed
Leung 2003
-
- Leung DYM, Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2003;361:151‐60. - PubMed
Lewis‐Jones 2001
-
- Lewis‐Jones MS, Finlay AY, Dykes PJ. The Infants' Dermatitis Quality of Life Index. British Journal of Dermatology 2001;144:104‐10. - PubMed
Neame 1995
-
- Neame RL, Berth‐Jones J, Kurinczuk JJ, Graham‐Brown RAC. Prevalence of atopic dermatitis in Leicester: a study of methodology and examination of possible ethnic variations. British Journal of Dermatology 1995;132:772‐7. - PubMed
NICE 2004
-
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Technology appraisal guidance 82: tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for atopic eczema. http://www.nice.org.uk/download.aspx?o=TA082guidance&template=downlo... (accessed 26th August 2004) 2004; Vol. London.
Stuetz 2001
-
- Stuetz A, Grassberger M, Meingassner JG. Pimecrolimus (Elidel, SDZ ASM 981) ‐ preclinical pharmacologic profile and skin sensitivity. Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery 2001;20(4):233‐41. - PubMed
Williams 1994
-
- Williams HC, Burney PGJ, Pembroke AC, Hay RH. The UK Working Party's diagnostic criteria for atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 1994;131(3):383‐96. - PubMed
Williams 1999
-
- Williams H, Robertson C, Stewart A, Ait‐Khaled N, Anabwani G, Anderson R, et al. Worldwide variations in the prevalence of symptoms of atopic eczema in the international study of asthma and allergies in childhood. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 1999;103(1):125‐38. - PubMed
Williams 2002
Williams 2003
-
- Williams H. 1% Pimecrolimus Cream for Atopic Dermatitis‐‐Reply. Archives of Dermatology Archives of Dermatology 2003;139(10):1370‐1. - PubMed
Williams 2005
-
- Williams HC. Clinical practice. Atopic dermatitis. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;352(22):2314‐24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

