Wound drains following thyroid surgery
- PMID: 17943885
- PMCID: PMC8991700
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006099.pub2
Wound drains following thyroid surgery
Abstract
Background: The nature and indications for thyroid surgery vary and a perceived risk of haemorrhage post-surgery is one reason why wound drains are frequently inserted. However when a significant bleed occurs, wound drains may become blocked and the drain does not obviate the need for surgery or meticulous haemostasis. The evidence in support of the use of drains post-thyroid surgery is unclear therefore and a systematic review of the best available evidence was undertaken.
Objectives: To determine the effects of inserting a wound drain during thyroid surgery, on wound complications, respiratory complications and mortality.
Search strategy: We searched the following databases: Cochrane Wounds Group Specialised Register and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (issue 1, 2007); MEDLINE (2005 to February 2007); EMBASE (2005 to February 2007); CINAHL (2005 to February 2007) using relevant search strategies.
Selection criteria: Only randomised controlled trials were eligible for inclusion. Quasi randomised studies were excluded. Studies with participants undergoing any form of thyroid surgery, irrespective of indications, were eligible for inclusion in this review. Studies involving people undergoing parathyroid surgery and lateral neck dissections were excluded. At least 80% follow up (till discharge) was considered essential.
Data collection and analysis: Studies were assessed for eligibility and data were extracted by two authors independently, differences were resolved by discussion. Studies were assessed for validity including criteria on whether they used a robust method of random sequence generation and allocation concealment. Missing and unclear data were resolved by contacting the study authors.
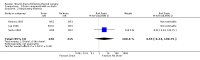
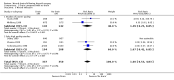
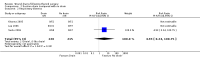
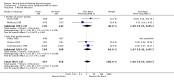
Main results: 13 eligible studies were identified (1646 participants). 11 studies compared drainage with no drainage and found no significant difference in re-operation rates; incidence of respiratory distress and wound infections. Post-operative wound collections needing aspiration or drainage were significantly reduced by drains (RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.27 to 0.97), but a further analysis of the 4 high quality studies showed no significant difference (RR 1.82, 95% CI 0.51 to 6.46). Hospital stay was significantly prolonged in the drain group (WMD 1.18 days, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.63).Eleven studies compared suction drain with no drainage and found no significant difference in re-operation rates; incidence of respiratory distress and wound infection rates. The incidence of collections that required aspiration or drainage without formal re-operation was significantly less in the drained group (RR 0.48, 95% CI 0.25 to 0.92). However, further analysis of only high quality studies showed no significant difference (RR 1.78, 95% CI 0.44 to 7.17). Hospital stay was significantly prolonged in the drain group (WMD 1.20 days, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.63). One study compared open drain with no drain. No participant in either group required re-operation. No data were available regarding the incidence of respiratory distress, wound infection and pain. The incidence of collections needing aspiration or drainage without re-operation was not significantly different between the groups and there was no significant difference in length of hospital stay. One study compared suction drainage with passive closed drainage. None of the participants in the study needed re-operation and data regarding other outcomes were not available. Two studies (180 participants) compared open drainage with suction drainage. One study reported wound infections and minor wound collections, both were not significantly different. The other study reported wound collections requiring intervention and hospital stay; both were not significantly different. None of the participants in either study required re-operation. Data regarding other outcomes were not available.
Authors' conclusions: There is no clear evidence that using drains in patients undergoing thyroid operations significantly improves patient outcomes and drains may be associated with an increased length of hospital stay. The existing evidence is from trials involving patients having goitres without mediastinal extension, normal coagulation indices and the operation not involving any lateral neck dissection for lymphadenectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures


















Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006099
Similar articles
-
Prophylactic abdominal drainage for pancreatic surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 21;6(6):CD010583. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010583.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 18;12:CD010583. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010583.pub5. PMID: 29928755 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prophylactic abdominal drainage for pancreatic surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 18;12(12):CD010583. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010583.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 May 16;5:CD010583. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010583.pub6. PMID: 34921395 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Negative pressure wound therapy for surgical wounds healing by primary closure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 26;4(4):CD009261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009261.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35471497 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic abdominal drainage for pancreatic surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 21;10(10):CD010583. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010583.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 21;6:CD010583. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010583.pub4. PMID: 27764898 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Wound drainage after axillary dissection for carcinoma of the breast.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Oct 20;2013(10):CD006823. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006823.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24158902 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prophylactic Wound Drainage in Renal Transplantation: A Systematic Review.Transplant Direct. 2019 Jun 27;5(7):e468. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000000908. eCollection 2019 Jul. Transplant Direct. 2019. PMID: 31334342 Free PMC article.
-
Wound complications and clinical results of electrocautery versus a scalpel to create a cutaneous flap in thyroidectomy: a prospective randomized trial.Surg Today. 2011 Aug;41(8):1041-8. doi: 10.1007/s00595-010-4435-5. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Surg Today. 2011. PMID: 21773891 Clinical Trial.
-
Abdominal drainage to prevent intraperitoneal abscess after appendectomy for complicated appendicitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 11;4(4):CD010168. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010168.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40214287
-
Prophylactic abdominal drainage for pancreatic surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 21;6(6):CD010583. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010583.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 18;12:CD010583. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010583.pub5. PMID: 29928755 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Is Prophylactic Antibiotic Therapy Needed in Thyroidectomy?Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Dec;74(Suppl 3):5769-5772. doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-02393-3. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36742545 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
De Salvo 1998 {published data only}
-
- Salvo L, Razzetta F, Tassone U, Arezzo A, Mattioli FP. [The role of drainage and antibiotic prophylaxis in thyroid surgery]. Minerva Chirurgica 1998;53(11):895‐8. - PubMed
Debry 1999 {published data only}
-
- Debry C, Renou G, Fingerhut A. Drainage after thyroid surgery: a prospective randomized study. The Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1999;113(1):49‐51. - PubMed
Giovannini 1999 {published data only}
-
- Giovannini C, Milito R, Pronio A, Santella S, Montesani C. Use of drainage in thyroid surgery. Chirurgia 1999;12(6):419‐21.
Hurtado‐Lopez 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hurtado‐Lopez LM, Lopez‐Romero S, Rizzo‐Fuentes C, Zaldivar‐Ramirez FR, Cervantes‐Sanchez C. Selective use of drains in thyroid surgery. Head and Neck 2001;23(3):189‐93. - PubMed
Khanna 2005 {published data only}
Lee 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lee SW, Choi EC, Lee YM, Lee JY, Kim SC, Koh YW. Is lack of placement of drains after thyroidectomy with central neck dissection safe? A prospective, randomized study. Laryngoscope 2006;116(9):1632‐5. - PubMed
Peix 1992 {published data only}
-
- Peix JL, Teboul F, Feldman H, Massard JL. Drainage after thyroidectomy: a randomized clinical trial. International Surgery 1992;77(2):122‐4. - PubMed
Pezzullo 2001 {published data only}
-
- Pezzullo L, Chiofalo MG, Caraco C, Marone U, Celentano E, Mozzillo N. Drainage in thyroid surgery: a prospective randomised clinical study. Chirurgia Italiana 2001;53(3):345‐7. - PubMed
Schoretsanitis 1998 {published data only}
-
- Schoretsanitis G, Melissas J, Sanidas E, Christodoulakis M, Vlachonikolis JG, Tsiftsis DD. Does draining the neck affect morbidity following thyroid surgery?. American Surgeon 1998;64(8):778‐80. - PubMed
Schwarz 1996 {published data only}
-
- Schwarz W, Willy C, Ndjee C. [Gravity or suction drainage in thyroid surgery? Control of efficacy with ultrasound determination of residual hematoma]. Langenbecks Archiv fur Chirurgie 1996;381(6):337‐42. - PubMed
Suslu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Suslu N, Vural S, Oncel M, Demirca B, Gezen FC, Tuzun B, et al. Is the insertion of drains after uncomplicated thyroid surgery always necessary?. Surgery Today 2006;36(3):215‐8. - PubMed
Teboul 1992 {published data only}
-
- Teboul F, Peix JL, Guibaud L, Massard JL, Ecochard R. [Prophylactic drainage after thyroidectomy: a randomized trial]. Annales de Chirurgie 1992;46(10):902‐4. - PubMed
Tubergen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Tubergen D, Moning E, Richter A, Lorenz D. [Assessment of drain insertion in thyroid surgery?]. Zentralblatt fur Chirurgie 2001;126(12):960‐3. - PubMed
Whilborg 1998 {published data only}
-
- Wihlborg O, Bergljung L, Martensson H. To drain or not to drain in thyroid surgery. A controlled clinical study. Archives of Surgery 1988;123(1):40‐1. - PubMed
Willy 1998 {published data only}
-
- Willy C, Steinbronn S, Sterk J, Gerngross H, Schwarz W. Drainage systems in thyroid surgery: a randomised trial of passive and suction drainage. European Journal of Surgery 1998;164(12):935‐40. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ayyash 1991 {published data only}
-
- Ayyash K, Khammash M, Tibblin S. Drain vs. no drain in primary thyroid and parathyroid surgery. European Journal of Surgery 1991;157(2):113‐4. - PubMed
Kristoffersson 1986 {published data only}
-
- Kristoffersson A, Sandzen B, Jarhult J. Drainage in uncomplicated thyroid and parathyroid surgery. British Journal of Surgery 1986;73(2):121‐2. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Mok 1992 {published data only}
-
- Mok CO, King WWK, Paterson‐Brown S, Mitchell RD, Li AKC. Suction drainage after thyroidectomy – is it necessary?. Third International Conference on Head and Neck Cancer, San Francisco. San Francisco, 1992.
Additional references
Abbas 2001
-
- Abbas G, Dubner S, Heller KS. Re‐operation for bleeding after thyroidectomy and parathyroidectomy. Head and Neck 2001;23(7):544‐6. - PubMed
Affleck 2003
-
- Affleck BD, Swartz K, Brennan J. Surgical considerations and controversies in thyroid and parathyroid surgery. Otolaryngology Clinics of North America 2003;36(1):159‐87. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ardito 1999
-
- Ardito G, Revelli L, Guidi ML, Murazio M, Lucci C, Modugno P, et al. [Drainage in thyroid surgery]. Annali Italiani di Chirurgia 1999;70(4):511‐6; discussion 516‐7. - PubMed
Brander 1991
-
- Brander A, Viikinkoski P, Nickels J, Kivisaari L. Thyroid gland: US screening in a random adult population. Radiology 1991;181(3):683‐7. - PubMed
Coello 1997
-
- Coello R, Glynn JR, Gaspar C, Picazo JJ, Fereres J. Risk factors for developing clinical infection with methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) amongst hospital patients initially only colonized with MRSA. The Journal of Hospital Infection 1997;37(1):39‐46. - PubMed
Collis 2005
-
- Collis N, McGuiness CM, Batchelor AG. Drainage in breast reduction surgery: a prospective randomised intra‐patient trail. British Journal of Plastic Surgery 2005;58(3):286‐9. - PubMed
Coress 2005
-
- Association of Surgeons of Great Britain and Ireland. He was speechless.... Confidential reporting systems in surgery (CORESS) December 2005. [Ref 013]
Corsten 2005
-
- Corsten M, Johnson S, Alherabi A. Is suction drainage an effective means of preventing hematoma in thyroid surgery? A meta‐analysis. Journal of Otolaryngology 2005;34(6):415‐7. - PubMed
Dackiw 2004
-
- Dackiw AP, Zeiger M. Extent of surgery for differentiated thyroid cancer. Surgical Clinics of North America. 2004;84(3):817‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Daou 1997
-
- Daou R. [Thyroidectomy without drainage]. Chirurgie, memoires de l'Academie de chirurgie 1997;122(7):408‐10. - PubMed
DeMets 1987
-
- DeMets DL. Methods for combining randomized clinical trials: strengths and limitations. Statistics in Medicine 1987;6(3):341‐50. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Ernst 1997
-
- Ernst R, Wiemer C, Rembs E, Friemann J, Theile A, Schafer K, et al. Local effects and changes in wound drainage in the free peritoneal cavity. Langenbecks Archiv fur Chirurgie 1997;382(6):380‐92. - PubMed
Farquharson 2005
-
- Farquharson M, Moran B. Surgery of the neck. In: Farquharson M, Moran B editor(s). Farquharson's Textbook of Operative General Surgery. 9. London: Hodder Arnold Publication, 2005:165‐7. [ISBN‐13:9780340814963]
Fredrickson 1998
-
- Fredrickson JM. Surgical Management of parathyroid disorder. In: Summers GW, Cummings CW, Fredrickson J M, Harker LA, Krause CJ, Richardson MA, et al. editor(s). Otolaryngology‐Head and Neck Surgery. 3. Vol. 3, Philadelphia: Mosby Year Book, Inc, 1998:2524‐5.
Friguglietti 2003
-
- Friguglietti CU, Lin CS, Kulcsar MA. Total thyroidectomy for benign thyroid disease.. Laryngoscope 2003;113(10):1820‐6. - PubMed
Gavilán 2002
-
- Gavilán J, Herranz J, Desanto LW, Gavilán C. Surgical Technique. In: Gavilán J, Herranz J, Desanto LW, Gavilán C editor(s). Functional and Selective Neck Dissection. New York: Thieme Medical Publishers, 2002:104‐5.
Healy 1989
-
- Healy DA, Keyser J, 3rd, Holcomb GW, 3rd, Dean RH, Smith BM. Prophylactic closed suction drainage of femoral wounds in patients undergoing vascular reconstruction. Journal of Vascular Surgery 1989;10(2):166‐8. - PubMed
HES 2006
-
- Department of Health. Hospital Episode Statistics. http://www.hesonline.nhs.uk/Ease/servlet/ContentServer?siteID=1937&c... Accessed 11 December 2006.
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2005
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews for Interventions 4.2.4 [updated March 2005]. http://www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook/hbook.htm (accessed 2005).
Hollis 1999
Horan 1992
-
- Horan TC, Gaynes RP, Martone WJ, Jarvis WR, Emori TG. CDC definitions of nosocomial surgical site infections, 1992: a modification of CDC definitions of surgical wound infections. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology 1992;13(10):606‐8. - PubMed
Huang 2005
-
- Huang SM, Lee CH, Chou FF, Liaw KY, Wu TC. Characteristics of thyroidectomy in Taiwan. Journal of Formosan Medical Association = Taiwan yi zhi 2005;104(1):6‐11. - PubMed
Hurtado‐Lopez 2002
-
- Hurtado‐Lopez LM, Zaldivar‐Ramirez FR, Basurto Kuba E, Pulido Cejudo A, Garza Flores JH, Munoz Solis O, et al. Causes for early reintervention after thyroidectomy. Medicine Science Monitor 2002;8(4):CR247‐50. - PubMed
Karayacin 1997
-
- Karayacin K, Besim H, Ercan F, Hamamci O, Korkmaz A. Thyroidectomy with and without drains. East African Medical Journal 1997;74(7):431‐2. - PubMed
Kjaergard 2001
-
- Kjaergard LL, Villumsen J, Gluud C. Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomized trials in meta‐analyses. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;135(11):982‐9. - PubMed
Knudsen 2000
-
- Knudsen N, Bulow I, Jorgensen T, Laurberg P, Ovesen L, Perrild H. Goitre prevalence and thyroid abnormalities at ultrasonography: a comparative epidemiological study in two regions with slightly different iodine status. Clinical Endocrinology 2000;53(4):479‐85. - PubMed
Macaskill 2001
-
- Macaskill P, Walter SD, Irwig L. A comparison of methods to detect publication bias in meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(4):641‐54. - PubMed
Mannell 1989
-
- Mannell A. Respiratory obstruction after thyroidectomy. A report of 2 cases. South African Journal of Surgery 1989;27(4):141‐3. - PubMed
Martis 1971
-
- Martis C, Athanassiades S. Post‐thyroidectomy laryngeal edema. A survey of fifty‐four cases. Amercian Journal of Surgery 1971;122(1):58‐60. - PubMed
Miccoli 2004
-
- Miccoli P, Materazzi G. Minimally invasive, video‐assisted thyroidectomy (MIVAT). Surgical Clinics of North America 2004;84(3):735‐41. - PubMed
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, Tugwell P, Klassen TP. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352(9128):609‐13. - PubMed
Okeke 2005
-
- Okeke IN, Laxminarayan R, Bhutta ZA, Duse AG, Jenkins P, O'Brien TF, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in developing countries. Part I: recent trends and current status. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2005;5(8):481‐93. - PubMed
Palestini 2005
-
- Palestini N, Tulletti V, Cestino L, Durando R, Freddi M, Sisti G, et al. [Post‐thyroidectomy cervical hematoma]. Minerva Chirurgica 2005;60(1):37‐46. - PubMed
Parker 2001
-
- Parker MJ, Roberts C. Closed suction surgical wound drainage after orthopaedic surgery. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 4. [Art. No.: CD001825. DOI: 10.1002/14651858] - PubMed
Pino 2004
-
- Pino Rivero V, Pardo Romero G, Gonzalez Palomino A, Trinidad Ruiz G, Marcos Garcia M, Blasco Huelva A. [Cervical abscess after hemithyroidectomy. An unusual complication]. Anales otorrinolaringologicos Ibero‐americanos 2004;31(3):231‐6. - PubMed
Pothier 2005
-
- Pothier DD. The use of drains following thyroid and parathyroid surgery: a meta‐analysis. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 2005;119(9):669‐71. - PubMed
Riehl 1995
-
- Riehl J, Kierdorf H, Schmitt H, Suiter T, Sieberth HG. [Prevalence of goiter in the Aachen area. Ultrasound volumetry of the thyroid gland of 1,336 adults in an endemic goiter region]. Ultraschall in der Medizin 1995;16(2):84‐9. - PubMed
Rios 2005
-
- Rios Zambudio A, Rodriguez Gonzalez JM, Galindo Fernandez PJ, Montoya Tabares MJ, Canteras Jordana M, Parrilla Paricio P. Clinical recurrence of multinodular goiter after surgery. A multivariate study on the risk factors. Revista clinica espanola. 2005;205(1):9‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rosato 2004
-
- Rosato L, Avenia N, Bernante P, Palma M, Gulino G, Nasi PG, et al. Complications of thyroid surgery: analysis of a multicentric study on 14,934 patients operated on in Italy over 5 years. World Journal of Surgery 2004;28(3):271‐6. - PubMed
Sanabria 2007
-
- Sanabria A, Carvalho AL, Silver CE, Rinaldo A, Shaha AR, Kowalski LP, et al. Routine drainage after thyroid surgery ‐ A meta‐analysis. Journal of Surgical Oncology 2007;96(3):273‐80. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. Journal of American Medical Association 1995;273(5):408‐12. - PubMed
Scott‐Coombes 2005
-
- Scott‐Coombes DM, Young A E. The Aird's Companion in Surgical Studies. In: Burnand K, Young AE, Lucas J editor(s). The Aird's Companion in Surgical Studies. 3rd Edition. Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2005:401‐2. [ISBN 0443072116]
Shaha 1993
-
- Shaha AR, Jaffe BM. Selective use of drains in thyroid surgery. Journal of Surgical Oncology 1993;52(4):241‐3. - PubMed
Shaha 1994
-
- Shaha AR, Jaffe BM. Practical management of post‐thyroidectomy hematoma. Journal of Surgical Oncology 1994;57(4):235‐8. - PubMed
Shaheen 1997
-
- Shaheen OH. The thyroid gland. In: John Hibbert editor(s). Scott‐Brown's Otolaryngology : Laryngology and Head & Neck Surgery. 6. Vol. 5, Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd, 1997:18/9‐18/10.
SIGN
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Search filters. http://www.sign.ac.uk/methodology/filters.html#random (accessed 27 February 2007).
SIGN 2006
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines network. Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Surgery Section 4: Indications for surgical antibiotic prophylaxis. http://www.sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/45/section4.html July 2000; Vol. Sign Publication No.45, issue Section 4. [ISBN 1899893 22 9]
Soleto 2003
-
- Soleto L, Pirard M, Boelaert M, Peredo R, Vargas R, Gianella A, et al. Incidence of surgical‐site infections and the validity of the National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System risk index in a general surgical ward in Santa Cruz, Bolivia. Infection Control and hospital Epidemiology: the official journal of the Society of Hospital Epidemiologists of America 2003;24(1):26‐30. - PubMed
Tabaqchali 1999
Teng 2002
-
- Teng X, Hu F, Teng W, Wang H, Shong S, Shan Z, et al. The study of thyroid diseases in a community not using iodized salt. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002;36(3):176‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

