Antiplatelet therapy for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage
- PMID: 17943892
- PMCID: PMC8919458
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006184.pub2
Antiplatelet therapy for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage
Abstract
Background: Secondary ischaemia is a frequent cause of poor outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH). Besides vasospasm, platelet aggregation seems to play a role in the pathogenesis of secondary ischaemia. Experimental studies have suggested that antiplatelet agents can prevent secondary ischaemia.
Objectives: To determine whether antiplatelet agents change outcome in patients with aneurysmal SAH.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Stroke Group Trials Register (last searched August 2006), MEDLINE (1966 to August 2006) and EMBASE databases (1980 to August 2006). We also searched reference lists of identified trials.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing any antiplatelet agent with control in patients with aneurysmal SAH.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted the data and assessed trial quality. Relative risks (RR) were calculated with regard to poor outcome, case fatality, secondary ischaemia, haemorrhagic intracranial complications and aneurysmal rebleeding according to the intention-to-treat principle. In case of a statistically significant primary analysis, a worst case analysis was performed.
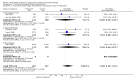
Main results: Seven RCTs were included in the review, totalling 1385 patients. Four of these trials met the criteria for good quality studies. For any antiplatelet agent there were reductions of a poor outcome (RR 0.79, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.62 to 1.01) and secondary brain ischaemia (RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.56 to 1.22) and more intracranial haemorrhagic complications (RR 1.36, 95% CI 0.59 to 3.12), but none of these differences were statistically significant. There was no effect on case fatality (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.37) or aneurysmal rebleeding (RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.38). For individual antiplatelet agents, only ticlopidine was associated with statistically significant fewer occurrences of a poor outcome (RR 0.37, 95% CI 95% CI 0.14 to 0.98) but this estimate was based on only one small RCT.
Authors' conclusions: This review shows a trend towards better outcome in patients treated with antiplatelet agents, possibly due to a reduction in secondary ischaemia. However, results were not statistically significant, thus no definite conclusions can be drawn. Also, antiplatelet agents could increase the risk of haemorrhagic complications. On the basis of the current evidence treatment with antiplatelet agents in order to prevent secondary ischaemia or poor outcome cannot be recommended.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors were involved in the organisation and writing of two of the included RCTs (Hop 2000; van den Bergh 2006).
Figures








Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006184
References
References to studies included in this review
Hop 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hop JW, Rinkel GJE, Algra A, Berkelbach van der Sprenkel JW, Gijn J. Randomized pilot trial of postoperative aspirin in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 2000;54:872‐8. - PubMed
Mendelow 1982 {published data only}
-
- Mendelow AD, Stockdill G, Steers AJW, Hayes J, Gillingham FJ. Double‐blind trial of aspirin in patients receiving tranexamic acid for subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta Neurochirurgica 1982;62:195‐202. - PubMed
Ono 1984 {published data only}
-
- Ono H, Mizukami M, Kitamura K, Kikuchi H. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. Agents and Actions Supplements 1984;15:259‐72. - PubMed
Shaw 1985 {published data only}
-
- Shaw MDM, Foy PM, Conway M, Pickard JD, Maloney P, Spillane JA, et al. Dipyridamole and postoperative ischemic deficits in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgery 1985;63:699‐703. - PubMed
Suzuki 1989 {published data only}
-
- Suzuki S, Sano K, Handa H, Asano T, Tamura A, Yonekawa Y, et al. Clinical study of OKY‐046, a thromboxane synthetase inhibitor, in prevention of cerebral vasospasms and delayed cerebral ischaemic symptoms after subarachnoid haemorrhage due to aneurysmal rupture: a randomized double‐blind study. Neurological Research 1989;11:79‐88. - PubMed
Tokiyoshi 1991 {published data only}
-
- Tokiyoshi K, Ohnishi T, Nii Y. Efficacy and toxicity of thromboxane synthetase inhibitor for cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surgical Neurology 1991;36:112‐8. - PubMed
van den Bergh 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bergh WM, Algra A, Dorhout Mees SM, Kooten F, Dirven CM, Gijn J, et al. Randomized controlled trial of acetylsalicylic acid in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: the MASH Study. Stroke 2006;37:2326‐30. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Fujita 1990 {published data only}
-
- Fujita K, Shirakuni T, Ehara K, Tamaki N, Matsumoto S. Prevention of the symptomatic vasospasm (SV) by antiplatelet agent (ticlopidine) and prophylactic hypervolemic hemodilution therapy ‐ evaluated by transcranial doppler sonography (TCD). Stroke 1990;21 Suppl I:1‐68.
Hirashima 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hirashima Y, Endo S, Nukui H, Kobayashi N, Takaku A. Effect of a platelet‐activating factor receptor antagonist, E5880, on cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage ‐ open clinical trial to investigate efficacy and safety. Neurologia medico‐chirurgica 2001;41(4):165‐76. - PubMed
Mizukami 1981 {published data only}
-
- Mizukami M, Kikuchi H, Ono H, Taneda M. Randomized study of ticlopidine on cerebral vasospasm following ruptured aneurysm. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1981;46:307.
Niemi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Niemi T, Tanskanen P, Taxell C, Juvela S, Randell T, Rosenberg P. Effects of nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs on hemostasis in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology 1999;11(3):188‐94. - PubMed
Suzuki 1981 {published data only}
-
- Suzuki S, Sobata E, Iwabuchi T. Prevention of cerebral ischemic symptoms in cerebral vasospasm with trapidil, an antagonist and selective synthesis inhibitor of thromboxane A2. Neurosurgery 1981;9:679‐85. - PubMed
Suzuki 1985 {published data only}
-
- Suzuki S, Iwabuchi T, Tanaka T, Kanayama S, Ottomo M, Hatanaka M, et al. Prevention of cerebral vasospasm with OKY‐046, an imidazole derivative and a thromboxane synthetase inhibitor: a preliminary co‐operative clinical study. Acta Neurochirurgica 1985;77:133‐41. - PubMed
Tani 1984 {published data only}
-
- Tani E, Maeda Y, Fukumori T, Nakano M, Kochi N, Morimura T, et al. Effect of selective inhibitor of thromboxane A2 synthetase on cerebral vasospasm after early surgery. Journal of Neurosurgery 1984;61:24‐9. - PubMed
Yano 1993 {published data only}
-
- Yano K, Kuroda T, Tanabe Y, Yamada H. Preventive therapy against delayed cerebral ischaemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: trials of thromboxane A2 synthetase inhibitor and hyperdynamic therapy. Acta Neurochirurgica 1993;125:15‐9. - PubMed
Additional references
ACROSS 2000
-
- [No authors listed]. Epidemiology of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in Australia and New Zealand: incidence and case fatality from the Australasian Cooperative Research on Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Study (ACROSS). Stroke 2000;31:1843‐50. - PubMed
Brilstra 2000
-
- Brilstra EH, Rinkel GJE, Algra A, Gijn J. Rebleeding, secondary ischemia, and timing of operation in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 2000;55:1656‐60. - PubMed
Cosmi 2001
de Rooij 2007
-
- Rooij NK, linn FHH, Plas JAP, Algra A, Rinkel GJE. Incidence of subarachnoid hemorrhage: a ten year update of a systematic review with emphasis of role of region, gender, age and time trend. In preparation.
Deeks 2001
-
- Deeks JJ, Altman DG, Bradburn MJ. Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combining results from several studies in meta‐analysis. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic reviews in health care: meta‐analysis in context. 2nd Edition. London: BMJ Publication Group, 2001.
Dorsch 1995
-
- Dorsch NW. Cerebral arterial spasm: a clinical review. British Journal of Neurosurgery 1995;9:403‐12. - PubMed
Hirashima 2005
-
- Hirashima Y, Hamada H, Kurimoto M, Origasa H, Endo S. Decrease in platelet count as an independent risk factor for symptomatic vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgery 2005;102:882‐7. - PubMed
Honma 1989
-
- Honma Y, Clower BR, Haining JL, Smith RR. Comparison of intimal platelet accumulation in cerebral arteries in two experimental models of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 1989;24:487‐90. - PubMed
Hop 1997
-
- Hop JW, Rinkel GJE, Algra A, Gijn J. Case‐fatality rates and functional outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review. Stroke 1997;28:660‐4. - PubMed
Juvela 1991
-
- Juvela S, Hillbom M, Kaste M. Platelet thromboxane release and delayed cerebral ischemia in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgery 1991;74:386‐92. - PubMed
Juvela 1995
-
- Juvela S. Aspirin and delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgery 1995;82:945‐52. - PubMed
Okhuma 1991
-
- Okhuma H, Suzuki S, Kimura M, Sobata E. Role of platelet function in symptomatic cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 1991;22:854‐9. - PubMed
Okhuma 1993
-
- Okhuma H, Ogane K, Fujita S, Manabe H, Suzuki S. Impairment of anti‐platelet‐aggregating activity of endothelial cells after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 1993;24:1541‐6. - PubMed
Patrono 1994
-
- Patrono C. Aspirin as an antiplatelet drug. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330:1287‐94. - PubMed
Rabinstein 2004
-
- Rabinstein AA, Friedman JA, Weigand SD, McClelland RL, Fulgham JR, Manno EM, et al. Predictors of cerebral infarction in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 2004;35:1862‐6. - PubMed
Rinkel 2005
-
- Rinkel GJ, Feigin VL, Algra A, Bergh WM, Vermeulen M, Gijn J. Calcium antagonists for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 1. [Art. No.: CD000277. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000277.pub3] - PubMed
Roos 2000
Toussaint 2004
-
- Toussaint LG, Friedman JA, Wijdicks EFM, Piepgras DG, Pichelmann MA, McIver JI, et al. Influence of aspirin on outcome following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of Neurosurgery 2004;101:921‐5. - PubMed
van der Schaaf 2002
-
- Schaaf IC, Ruigrok YM, Rinkel GJE, Algra A, Gijn J. Study design and outcome measures in studies on aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 2002;33:2043‐6. - PubMed
Vane 2003
-
- Vane JR, Botting RM. The mechanism of action of aspirin. Thrombosis Research 2003;110:255‐8. - PubMed
Vinge 1988
-
- Vinge E, Brandt L, Ljunggren B, Andersson KE. Thromboxane B2 levels in serum during continuous administration of nimodipine to patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 1988;19:644‐7. - PubMed
Weinberger 2005
-
- Weinberger J. Adverse effects and drug interactions of antithrombotic agents used in prevention of ischaemic stroke. Drugs 2005;65:461‐71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

