Evidence for internal and external binding sites on human tear lipocalin
- PMID: 17945179
- PMCID: PMC2129106
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2007.09.011
Evidence for internal and external binding sites on human tear lipocalin
Abstract
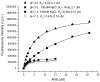
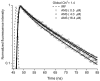
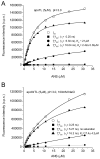
8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid (ANS) is widely used as a probe for locating binding sites of proteins. To characterize the binding sites of tear lipocalin (TL), we studied ANS binding to apoTL by steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence. Deconvolution of ANS binding revealed that two lifetime components, 16.99ns and 2.76ns at pH 7.3, have dissociation constants of 0.58muM and 5.7muM, respectively. At pH 3.0, the lifetime components show decreased affinities with dissociation constants of 2.42muM and approximately 21muM, respectively. Selective displacement of ANS molecules from the ANS-apoTL complex by stearic acid discriminates the internal and external binding sites. Dependence of the binding affinity on ionic strength under various conditions provides strong evidence that an electrostatic interaction is involved. Time-resolved fluorescence is a promising tool to segregate multiple binding sites of proteins.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

