Golf putt outcomes are predicted by sensorimotor cerebral EEG rhythms
- PMID: 17947315
- PMCID: PMC2375559
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.141630
Golf putt outcomes are predicted by sensorimotor cerebral EEG rhythms
Abstract
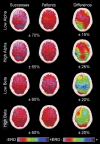
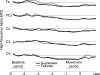
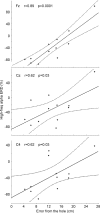
It is not known whether frontal cerebral rhythms of the two hemispheres are implicated in fine motor control and balance. To address this issue, electroencephalographic (EEG) and stabilometric recordings were simultaneously performed in 12 right-handed expert golfers. The subjects were asked to stand upright on a stabilometric force platform placed at a golf green simulator while playing about 100 golf putts. Balance during the putts was indexed by body sway area. Cortical activity was indexed by the power reduction in spatially enhanced alpha (8-12 Hz) and beta (13-30 Hz) rhythms during movement, referred to as the pre-movement period. It was found that the body sway area displayed similar values in the successful and unsuccessful putts. In contrast, the high-frequency alpha power (about 10-12 Hz) was smaller in amplitude in the successful than in the unsuccessful putts over the frontal midline and the arm and hand region of the right primary sensorimotor area; the stronger the reduction of the alpha power, the smaller the error of the unsuccessful putts (i.e. distance from the hole). These results indicate that high-frequency alpha rhythms over associative, premotor and non-dominant primary sensorimotor areas subserve motor control and are predictive of the golfer's performance.
Figures
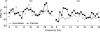

References
-
- Arroyo S, Lesser RP, Gordon B, Uematso S, Jackson D, Webber R. Functional significance of the mu rhythm of human cortex: an electrophysiologic study with subdural electrodes. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1993;87:76–87. - PubMed
-
- Ashe J, Lungu OV, Basford AT, Lu X. Cortical control of motor sequences. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006;16:213–221. - PubMed
-
- Babiloni F, Babiloni C, Carducci F, Fattorini L, Onorati P, Urbano A. Spline Laplacian estimate of EEG potentials over a realistic magnetic resonance-constructed scalp surface model. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1996;98:363–373. - PubMed
-
- Babiloni F, Carducci F, Babiloni C, Urbano A. Improved realistic Laplacian estimate of highly-sampled EEG potentials by regularization techniques. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1998;106:336–343. - PubMed
-
- Babiloni C, Carducci F, Cincotti F, Rossini PM, Neuper C, Pfurtscheller G, Babiloni F. Human movement-related potentials vs. desynchronizationof EEG alpha rhythm: a high-resolution EEG study. Neuroimage. 1999;10:658–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

