Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings
- PMID: 17947576
- PMCID: PMC2601629
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1147241
Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings
Abstract
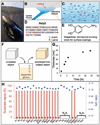
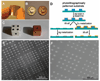
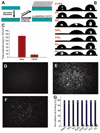
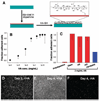
We report a method to form multifunctional polymer coatings through simple dip-coating of objects in an aqueous solution of dopamine. Inspired by the composition of adhesive proteins in mussels, we used dopamine self-polymerization to form thin, surface-adherent polydopamine films onto a wide range of inorganic and organic materials, including noble metals, oxides, polymers, semiconductors, and ceramics. Secondary reactions can be used to create a variety of ad-layers, including self-assembled monolayers through deposition of long-chain molecular building blocks, metal films by electroless metallization, and bioinert and bioactive surfaces via grafting of macromolecules.
Figures
Comment in
-
Bioinspired Coordination Micelles Integrating High Stability, Triggered Cargo Release, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Jan 11;9(1):80-91. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b09425. Epub 2016 Dec 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 27957858
References
-
- Ratner BD, Hoffman AS, editors. Biomaterials Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine. ed. 2. San Diego, CA: Elsevier Academic; 2004.
-
- Ahn J-H, et al. Science. 2006;314:1754. - PubMed
-
- Alivisatos P. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004;22:47. - PubMed
-
- Langer R. Science. 2001;293:58. - PubMed
-
- Love JC, Estroff LA, Kriebel JK, Nuzzo RG, Whitesides GM. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:1103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

