Regulation of histone modification and cryptic transcription by the Bur1 and Paf1 complexes
- PMID: 17948059
- PMCID: PMC2080810
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601887
Regulation of histone modification and cryptic transcription by the Bur1 and Paf1 complexes
Abstract
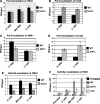
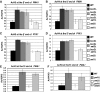
The Bur1-Bur2 and Paf1 complexes function during transcription elongation and affect histone modifications. Here we describe new roles for Bur1-Bur2 and the Paf1 complex. We find that histone H3 K36 tri-methylation requires specific components of the Paf1 complex and that K36 tri-methylation is more strongly affected at the 5' ends of genes in paf1delta and bur2delta strains in parallel with increased acetylation of histones H3 and H4. Interestingly, the 5' increase in histone acetylation is independent of K36 methylation, and therefore is mechanistically distinct from the methylation-driven deacetylation that occurs at the 3' ends of genes. Finally, Bur1-Bur2 and the Paf1 complex have a second methylation-independent function, since bur2delta set2delta and paf1delta set2delta double mutants display enhanced histone acetylation at the 3' ends of genes and increased cryptic transcription initiation. These findings identify new functions for the Paf1 and Bur1-Bur2 complexes, provide evidence that histone modifications at the 5' and 3' ends of coding regions are regulated by distinct mechanisms, and reveal that the Bur1-Bur2 and Paf1 complexes repress cryptic transcription through a Set2-independent pathway.
Figures


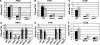
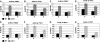
References
-
- Ausubel FA, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1997) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York: John Wiley & Sons
-
- Bannister AJ, Schneider R, Myers FA, Thorne AW, Crane-Robinson C, Kouzarides T (2005) Spatial distribution of di- and tri-methyl lysine 36 of histone H3 at active genes. J Biol Chem 280: 17732–17736 - PubMed
-
- Carrozza MJ, Li B, Florens L, Suganuma T, Swanson SK, Lee KK, Shia WJ, Anderson S, Yates J, Washburn MP, Workman JL (2005) Histone H3 methylation by Set2 directs deacetylation of coding regions by Rpd3S to suppress spurious intragenic transcription. Cell 123: 581–592 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

