The treatment of venous ulcers of the lower extremities
- PMID: 17948110
- PMCID: PMC2014806
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2007.11928324
The treatment of venous ulcers of the lower extremities
Abstract
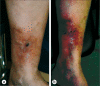
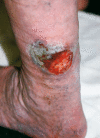
Venous hypertension from failure of proper venous valve function in the veins of thelower extremities causes changes over time in the microcirculation of the skin of the distal extremity. These changes set the stage for the development of a chronic nonhealing ulceration, which typically occurs at the ankle. The mainstay of treatment has been conservative, with compression dressings and elevation of the extremity. However, results have been less than satisfactory because of delay in healing and high recurrence rates after successful healing. Elimination of the venous hypertension should be the goal of therapy using more recent minimally invasive surgical techniques, including ablation of incompetent truncal veins with laser or radiofrequency energy and use of ultrasound-guided foam sclerosant injections to close incompetent perforator veins that are frequently found in or near the ulcer bed. This approach will shorten ulcer healing time and reduce recurrence rates as well as patient suffering and expense.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endovenous ablation of incompetent perforating veins is effective treatment for recalcitrant venous ulcers.J Vasc Surg. 2011 Sep;54(3):737-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.02.068. Epub 2011 Jun 12. J Vasc Surg. 2011. PMID: 21658887
-
Chronic venous ulcer: minimally invasive treatment of superficial axial and perforator vein reflux speeds healing and reduces recurrence.Ann Vasc Surg. 2013 Jan;27(1):75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2012.06.002. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Ann Vasc Surg. 2013. PMID: 23084734
-
Combined treatment with endovenous laser ablation and compression therapy of incompetent perforating veins for treatment of recalcitrant venous ulcers.Phlebology. 2017 Jun;32(5):307-315. doi: 10.1177/0268355515594075. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Phlebology. 2017. PMID: 26130052
-
Minimally invasive treatments for perforator vein insufficiency.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2016 Dec;6(6):593-598. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2016.11.12. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2016. PMID: 28123979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Why Venous Leg Ulcers Have Difficulty Healing: Overview on Pathophysiology, Clinical Consequences, and Treatment.J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 24;10(1):29. doi: 10.3390/jcm10010029. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33374372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lateral subfascial endoscopic perforating vein surgery as treatment for lateral perforating vein incompetence and venous ulceration.World J Surg. 2009 May;33(5):1093-8. doi: 10.1007/s00268-009-9921-9. World J Surg. 2009. PMID: 19189173
-
Blood Flow Analysis of the Great Saphenous Vein in the Su-Pine Position in Clinical Manifestations of Varicose Veins of Different Severities: Application of Phase-Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jan 5;12(1):118. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12010118. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35054283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rejan TJ. The epidemiology of leg ulcers. In: Westerhof W, editor. Leg Ulcers: Diagnosis and Treatment. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers BV; 1993. pp. 19–27.
-
- Baker SR, Stacey MC, Jopp-McKay AG, Hoskin SE, Thompson PJ. Epidemiology of chronic venous ulcers. Br J Surg. 1991;78(7):864–867. - PubMed
-
- Margolis DJ, Bilker W, Santanna J, Baumgarten M. Venous leg ulcer: incidence and prevalence in the elderly. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(3):381–386. - PubMed
-
- Phillips TJ. Chronic cutaneous ulcers: etiology and epidemiology. J Invest Dermatol. 1994;102(6):38S–41S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
