Canada's contribution to respiratory physiology and pathophysiology
- PMID: 17948138
- PMCID: PMC2677783
- DOI: 10.1155/2007/401795
Canada's contribution to respiratory physiology and pathophysiology
Figures
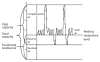
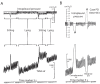
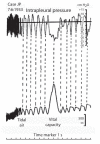

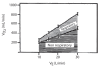
Similar articles
-
The development of ideas on the cardiac and respiratory complications of spinal deformities.Med Hist. 1977 Oct;21(4):397-410. doi: 10.1017/s002572730003903x. Med Hist. 1977. PMID: 337002 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In memoriam: Frederick E Hargreave (1938-2011).Thorax. 2011 Dec;66(12):1101-2. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-201141. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Thorax. 2011. PMID: 21998123 No abstract available.
-
Obituary Pierre Dejours.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009 Mar 31;166(1):1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2009.01.004. Epub 2009 Jan 22. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19429516 No abstract available.
-
Choking agents and chlorine gas - History, pathophysiology, clinical effects and treatment.Toxicol Lett. 2020 Mar 1;320:73-79. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.12.005. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Toxicol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31811912 Review.
-
Reflexes from the lungs and airways: historical perspective.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006 Aug;101(2):628-34. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00155.2006. Epub 2006 Apr 6. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006. PMID: 16601307 Review.
References
-
- Christie RV, Eldridge FL, McIlroy MB, Thomas JP. The effect of added elastic and non-elastic resistances on the pattern of breathing in normal subjects. Clin Sci (Lond) 1956;15:337–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

