Caenorhabditis elegans germ line: a model for stem cell biology
- PMID: 17948315
- PMCID: PMC2949268
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.21335
Caenorhabditis elegans germ line: a model for stem cell biology
Abstract
Like many stem cell systems, the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line contains a self-renewing germ cell population that is maintained by a niche. Although the exact cellular mechanism for self-renewal is not yet known, three recent studies shed considerable light on the cell cycle behavior of germ cells, including a support for significant and plastic renewal potential. This review brings together the results of the three recent cell-based studies, places them in the context of previous work, and discusses future perspectives for the field.
2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc
Figures

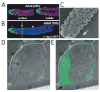
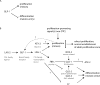

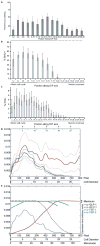
References
-
- Ambros V. Cell cycle-dependent sequencing of cell fate decisions in Caenorhabditis elegans vulva precursor cells. Development. 1999;126:1947–1956. - PubMed
-
- Austin J, Kimble J. glp-1 is required in the germ line for regulation of the decision between mitosis and meiosis in C. elegans. Cell. 1987;51:589–599. - PubMed
-
- Beanan M, Strome S. Characterization of a germ-line proliferation mutation in C. elegans. Development. 1992;116:755–766. - PubMed
-
- Berry L, Westlund B, Schedl T. Germ-line tumor formation caused by activation of glp-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans member of the Notch family of receptors. Development. 1997;124:925–936. - PubMed
-
- Brauchle M, Baumer K, Gonczy P. Differential activation of the DNA replication checkpoint contributes to asynchrony of cell division in C. elegans embryos. Curr Biol. 2003;13:819–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

