Effect of Scutellariae Radix extract on experimental dextran-sulfate sodium-induced colitis in rats
- PMID: 17948935
- PMCID: PMC4172740
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i42.5605
Effect of Scutellariae Radix extract on experimental dextran-sulfate sodium-induced colitis in rats
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of Scutellariae Radix extract (SRE) on ulcerative colitis (UC) in rats induced by dextran-sulfate sodium (DSS).
Methods: Colitis was induced in male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (170-180 g) by 4% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS, wt/v; MW 54000) in drinking water for 8 d. The treated rats received 4% DSS and SRE orally (100 mg/kg per day). Control rats received either tap water or SRE only. Macroscopic assessment which included body weight changes, fecal occult blood and stool consistency were determined daily. At the appointed time, the rats were sacrificed and the entire colons were removed. The colon length and the myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity were measured. The severity of colitis was graded by morphological and histological assessments. The ion transport activity of the colonic mucosa was assessed by electrophysiological technique.
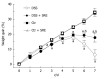
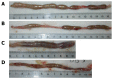
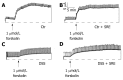
Results: Rats treated with oral administration of 4% DSS regularly developed clinical and macroscopic signs of colitis. Treatment with SRE relieved the symptoms, including the reduction in body weight, shortening and ulceration of the colon. Administration of SRE also significantly reduced the histological damage induced by DSS. Moreover, the I(SC) responses of the colonic mucosa to forskolin were suppressed after the induction of colitis. The stimulated ion transport activity of DSS-rats treated with SRE displayed significant improvement in the secretory responsiveness.
Conclusion: SRE was effective in treating acute DSS-induced ulcerative colitis, as gauged by reduced clinical disease, improved macroscopic and histological damage scores, and enhanced recovery of normal colonic secretory function.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Therapeutic effect of a hydroxynaphthoquinone fraction on dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 7;20(41):15310-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15310. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25386079 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of toll-like receptor 3 agonist poly I:C on intestinal mucosa and epithelial barrier function in mouse models of acute colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb 14;23(6):999-1009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.999. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28246473 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of processed Scutellaria baicalensis on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice.Int J Mol Med. 2005 Oct;16(4):667-72. Int J Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16142402
-
Effect of Eucommia ulmoides Leaf Extract on Chronic Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis in Mice.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(6):864-868. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00878. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 29863075
-
Induction of colitis and its analyses.2021 Sep 2 [updated 2022 Apr 5]. In: Nishihara S, Angata K, Aoki-Kinoshita KF, Hirabayashi J, editors. Glycoscience Protocols (GlycoPODv2) [Internet]. Saitama (JP): Japan Consortium for Glycobiology and Glycotechnology; 2021–. 2021 Sep 2 [updated 2022 Apr 5]. In: Nishihara S, Angata K, Aoki-Kinoshita KF, Hirabayashi J, editors. Glycoscience Protocols (GlycoPODv2) [Internet]. Saitama (JP): Japan Consortium for Glycobiology and Glycotechnology; 2021–. PMID: 37590676 Free Books & Documents. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Recent Progress in Traditional Chinese Medicines and Their Mechanism in the Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Apr 11;2022:3594210. doi: 10.1155/2022/3594210. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 May 24;2023:9869570. doi: 10.1155/2023/9869570. PMID: 35444784 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Exosomes Derived from Dendritic Cells Treated with Schistosoma japonicum Soluble Egg Antigen Attenuate DSS-Induced Colitis.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 14;8:651. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00651. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28959207 Free PMC article.
-
Multidirectional Pharma-Toxicological Study on Harpagophytum procumbens DC. ex Meisn.: An IBD-Focused Investigation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Feb 18;9(2):168. doi: 10.3390/antiox9020168. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32085616 Free PMC article.
-
The safety of flavocoxid, a medical food, in the dietary management of knee osteoarthritis.J Med Food. 2009 Oct;12(5):1143-8. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2008.0244. J Med Food. 2009. PMID: 19857081 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Huangqin-Tang and Ingredients in Modulating the Pathogenesis of Ulcerative Colitis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:7016468. doi: 10.1155/2017/7016468. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28690663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leong RW, Lau JY, Sung JJ. The epidemiology and phenotype of Crohn's disease in the Chinese population. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2004;10:646–651. - PubMed
-
- Ouyang Q, Tandon R, Goh KL, Ooi CJ, Ogata H, Fiocchi C. The emergence of inflammatory bowel disease in the Asian Pacific region. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005;21:408–413. - PubMed
-
- Leong RW, Lawrance IC, Ching JY, Cheung CM, Fung SS, Ho JN, Philpott J, Wallace AR, Sung JJ. Knowledge, quality of life, and use of complementary and alternative medicine and therapies in inflammatory bowel disease: a comparison of Chinese and Caucasian patients. Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49:1672–1676. - PubMed
-
- Lin CC, Shieh DE. The anti-inflammatory activity of Scutellaria rivularis extracts and its active components, baicalin, baicalein and wogonin. Am J Chin Med. 1996;24:31–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

