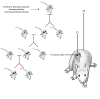
What is an epigenetic transgenerational phenotype? F3 or F2
- PMID: 17949945
- PMCID: PMC2249610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2007.09.001
What is an epigenetic transgenerational phenotype? F3 or F2
Abstract
The ability of an environmental exposure to induce an epigenetic transgenerational adult onset disease phenotype is discussed in the current mini-review in the context of defining this phenomenon and the associated reproductive toxicology. A gestating female (F0 generation) exposure to an environmental compound results in the F1 generation embryo and F2 generation germ-line being directly exposed, such that the F3 generation is the first not directly exposed to the environmental compound. In contrast, postnatal or adult exposure (F0 generation) results in the F1 generation germ-line being exposed, such that F2 generation is the first to not be directly exposed to the environmental compound. The unequivocal transgenerational transmission of an adult onset disease phenotype through the germ-line requires assessment of the F3 generation for embryonic exposure, and F2 generation for postnatal exposure. This is in contrast to a number of F1 and F2 generation studies referred to as transgenerational. The reproductive toxicology associated with this transgenerational phenotype generally involves the reprogramming of the germ-line epigenome. The biological phenomenon involved in this reproductive toxicology deals with embryonic gonadal development and germ-line differentiation, or postnatally the gametogenesis process and germ cell development. The ability of an environmental compound (e.g. endocrine disruptor) to promote this reprogramming of the germ-line appears to be the causal factor in the epigenetic transgenerational phenotype.
Figures
References
-
- Cesani MF, Orden B, Zucchi M, Mune MC, Oyhenart EE, Pucciarelli HM. Effect of undernutrition on the cranial growth of the rat. An intergenerational study. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174:129–35. - PubMed
-
- Klip H, Verloop J, van Gool JD, Koster ME, Burger CW, van Leeuwen FE. Hypospadias in sons of women exposed to diethylstilbestrol in utero: a cohort study. Lancet. 2002;359:1102–7. - PubMed
-
- Newbold RR, Padilla-Banks E, Jefferson WN. Adverse effects of the model environmental estrogen diethylstilbestrol are transmitted to subsequent generations. Endocrinology. 2006;147:S11–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous