Steatocholecystitis: the influence of obesity and dietary carbohydrates
- PMID: 17950329
- PMCID: PMC2431458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.04.042
Steatocholecystitis: the influence of obesity and dietary carbohydrates
Abstract
Introduction: We have recently demonstrated that obese and lean mice fed a high fat diet have increased gallbladder wall fat and decreased gallbladder contractility, cholecystosteatosis. Animal and human data also suggest that diets high in refined carbohydrates lead to gallstone formation. However, no data are available on the role of dietary carbohydrates on gallbladder wall fat and inflammation. Therefore, we tested the hypothesis that both obesity and dietary carbohydrates would increase gallbladder fat and cytokines, steatocholecystitis.
Methods: At 8 wk of age, 47 lean and 22 obese female mice were fed a 45% carbohydrate (CHO) diet while an equal number of lean and obese mice were fed a 75% CHO diet for 4 wk. All mice underwent cholecystectomy, and the gallbladders were snap-frozen. Individual and total lipids were measured by gas chromatography. Interleukin (IL)-1beta, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, and IL-6 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data were analyzed by analysis of variance and Tukey test.
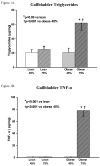
Results: Gallbladder total fat, triglycerides, and cholesterol were maximum (P < 0.001) in obese mice on the 75% CHO diet. Gallbladder TNF-alpha and IL-1beta as well as serum cholesterol levels showed a similar pattern (P < 0.001). Gallbladder saturated free fatty acids and IL-6 levels were highest (P < 0.001) in obese mice on the 45% CHO diet.
Conclusions: These data suggest that (1) both obesity and dietary carbohydrates increase gallbladder total fat, triglycerides, cholesterol, TNF-alpha, and IL-1beta and (2) obesity also increases gallbladder free fatty acids and IL-6. Therefore, we conclude that obesity is associated with steatocholecystitis and that a high carbohydrate diet exacerbates this phenomenon.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Steatocholecystitis and fatty gallbladder disease.Dig Dis Sci. 2009 Sep;54(9):1857-63. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0578-2. Epub 2008 Dec 18. Dig Dis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19093209 Review.
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty gallbladder disease: the influence of diet in lean and obese mice.J Gastrointest Surg. 2006 Feb;10(2):193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2005.07.009. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006. PMID: 16455450
-
High dietary carbohydrates decrease gallbladder volume and enhance cholesterol crystal formation.Surgery. 2007 May;141(5):654-9. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2006.11.008. Epub 2007 Feb 6. Surgery. 2007. PMID: 17462466
-
Shifts in diet from high fat to high carbohydrate improved levels of adipokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice fed a high-fat diet.Endocr J. 2010;57(1):39-50. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.k09e-046. Epub 2009 Oct 10. Endocr J. 2010. PMID: 19822999
-
[Obesity as a risk factor of non-alcoholic fatty gallbladder disease (cholicyststeatosis, steatocholecystitis)].Eksp Klin Gastroenterol. 2009;(8):80-93. Eksp Klin Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 20469684 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Steatocholecystitis and fatty gallbladder disease.Dig Dis Sci. 2009 Sep;54(9):1857-63. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0578-2. Epub 2008 Dec 18. Dig Dis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19093209 Review.
-
Comparative study on the effects of high fat diet and capsicum diet on the digestive organs of guinea pigs.Sci Rep. 2025 May 23;15(1):17886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93583-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40404945 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between temporal eating patterns and energy distribution patterns with gallstones: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES 2017-2018.BMC Public Health. 2024 Oct 29;24(1):2994. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20512-x. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39472867 Free PMC article.
-
Nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease.HPB (Oxford). 2007;9(4):312-8. doi: 10.1080/13651820701504157. HPB (Oxford). 2007. PMID: 18345311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Dietz WH, Vinicor F, Bales VS, et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA. 2003;289:76–79. - PubMed
-
- Farrell GC, Larter CZ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2006;43:S99–S112. - PubMed
-
- Goldblatt MI, Swartz-Basile DA, Al-Azzawi HH, Tran KQ, Nakeeb A, Pitt HA. Nonalcoholic fatty gallbladder disease: The influence of diet in lean and obese mice. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006;10:193–201. - PubMed
-
- Al-azzawi HA, Nakeeb A, Saxena R, Maluccio MA, Pitt HA. Cholecystosteatosis: An Explanation for Increased Cholecystectomy Rates. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007 in press. - PubMed
-
- Gilloteaux J, Tomasello LM, Elgison DA. Lipid deposits and lipo-mucosomes in human cholecystitis and epithelial metaplasia in chronic cholecystitis. Ultrastructural Pathology. 2003;27:313–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

