Antibody-mediated protection against genital herpes simplex virus type 2 disease in mice by Fc gamma receptor-dependent and -independent mechanisms
- PMID: 17950908
- PMCID: PMC2441821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jri.2007.08.004
Antibody-mediated protection against genital herpes simplex virus type 2 disease in mice by Fc gamma receptor-dependent and -independent mechanisms
Abstract
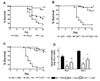
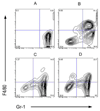
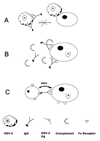
The ability of antibody (Ab) to modulate HSV pathogenesis is well recognized but the mechanisms by which HSV-specific IgG antibodies protect against genital HSV-2 disease are not well understood. The requirement for Ab interactions with Fcgamma receptors (FcgammaR) in protection was examined using a murine model of genital HSV-2 infection. IgG antibodies isolated from the serum of HSV-immune mice protected normal mice against HSV-2 disease when administered prior to genital HSV-2 inoculation. However, protection was significantly diminished in recipient mice lacking the gamma chain subunit utilized in FcgammaRI, FcgammaRIII, FcgammaRIV and FcepsilonRI receptors and in normal mice depleted of Gr-1(+) immune cell populations known to express FcgammaR, suggesting protection was largely mediated by an FcgammaR-dependent mechanism. To test whether neutralizing Ab might provide superior protection, a highly neutralizing HSV glycoprotein D (gD)-specific monoclonal antibody (mAb) was utilized. Similar to results with HSV-specific polyclonal IgG, administration of the gD-specific mAb did not prevent initial infection of the genital tract but resulted in lower virus loads in the vaginal epithelium and provided significant protection against disease and acute infection of the sensory ganglia; however, this protection was independent of host FcgammaR expression and was manifest in mice depleted of Gr-1(+) immune cells. Together, these data demonstrate that substantial Ab-mediated protection against genital HSV-2 disease could be achieved by either FcgammaR-dependent or -independent mechanisms. These studies suggest that HSV vaccines might need to elicit multiple, diverse antibody effector mechanisms to achieve optimal protection.
Figures

References
-
- Andoh T, Kuraishi Y. Direct action of immunoglobulin G on primary sensory neurons through Fc gamma receptor I. FASEB J. 2004;18:182–184. - PubMed
-
- Armour KL, Atherton A, Williamson LM, Clark MR. The contrasting IgG-binding interactions of human and herpes simplex virus Fc receptors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002;30:495–500. - PubMed
-
- Bourne N, Bravo FJ, Francotte M, Bernstein DI, Myers MG, Slaoui M, Stanberry LR. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 2 glycoprotein D subunit vaccines afford guinea pigs comparable protection against genital HSV-1 or HSV-2 disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2003;187:542–549. - PubMed
-
- Bourne N, Pyles RB, Bernstein DI, Stanberry LR. Modification of primary and recurrent genital herpes in guinea pigs by passive immunization. J. Gen. Virol. 2002;83:2797–2801. - PubMed
-
- Brown Z, Benedetti J, Ashley R, Burchett S, Selke S, Berry S, Vontver LA, Corey L. Neonatal herpes virus infection in relation to asymptomatic maternal infection at the time of delivery. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991;324:1247–1252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

