A novel role for the semaphorin Sema4D in the induction of allo-responses
- PMID: 17950916
- PMCID: PMC2278022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2007.07.014
A novel role for the semaphorin Sema4D in the induction of allo-responses
Abstract
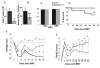
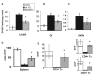
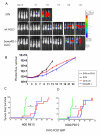
Sema4D (CD100), a member of the neuro-semaphorin family of proteins, has recently been shown to play a role in modulating certain immune responses. We tested the requirement of Sema4D expression on T cells in the induction of T cell allo-immune responses. Sema4D-/- T cells showed reduced expansion in vitro upon stimulation with allo-geneic antigen presenting cells (APCs) when compared to wild-type (wt) T cells. Similar in vitro results were observed using anti-Sema4D mAbs. Further studies demonstrated that the reduced proliferation was not due to intrinsic T cell defects, and that the cytotoxic functions were preserved. After allo-geneic bone marrow transplant (BMT), recipients of Sema4D-/- T cells showed reduced mortality and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) target organ damage. Allo-geneic dendritic cells (DCs) cocultured with Sema4D-/- responder T cells secreted less TNF-alpha and IL-12p70 compared to wt T cells. Similar reduction of DC function was observed with anti-Sema4D mAbs. Given the preservation of CTL function we evaluated graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) responses. When BALB/c recipient mice were challenged with the P815 murine mastocytoma cell line (H2(d)) the recipients of allo-geneic Sema4D-/- B6 T cells showed a significant improvement in tumor free survival when compared to syngeneic recipients, thus demonstrating preservation of GVL, albeit of a lesser magnitude than allo-geneic wt T cells. In summary, Sema4D plays a significant role in mediating in vitro and in vivo allo-geneic responses by modulating T cell-APC interactions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recipient-Derived Allo-iTregs Induced by Donor DCs Effectively Inhibit the Proliferation of Donor T Cells and Reduce GVHD.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2019 May;302(5):825-836. doi: 10.1002/ar.23972. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 30312018
-
Graft-versus-leukemia effect and graft-versus-host disease can be differentiated by cytotoxic mechanisms in a murine model of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.Blood. 1999 Apr 15;93(8):2738-47. Blood. 1999. PMID: 10194454
-
IL-11 separates graft-versus-leukemia effects from graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation.J Clin Invest. 1999 Aug;104(3):317-25. doi: 10.1172/JCI7111. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10430613 Free PMC article.
-
Alloreactivity and the predictive value of anti-recipient specific interleukin 2 producing helper T lymphocyte precursor frequencies for alloreactivity after bone marrow transplantation.Dan Med Bull. 2002 May;49(2):89-108. Dan Med Bull. 2002. PMID: 12064093 Review.
-
Th2 and Tc2 cells in the regulation of GVHD, GVL, and graft rejection: considerations for the allogeneic transplantation therapy of leukemia and lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2000 Jul;38(3-4):221-34. doi: 10.3109/10428190009087014. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000. PMID: 10830730 Review.
Cited by
-
Transmembrane semaphorins: Multimodal signaling cues in development and cancer.Cell Adh Migr. 2016 Nov;10(6):675-691. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2016.1197479. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Cell Adh Migr. 2016. PMID: 27295627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-α-Enhanced CD100/Plexin-B1/B2 Interactions Promote Natural Killer Cell Functions in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 3;8:1435. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01435. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29163508 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association study on hematopoietic stem cell transplantation reveals novel genomic loci associated with transplant outcomes.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 7;15:1280876. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1280876. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38384455 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell clonal tracking of persistent T-cells in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 10;14:1114368. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1114368. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36860867 Free PMC article.
-
CD8low CD100- T Cells Identify a Novel CD8 T Cell Subset Associated with Viral Control during Human Hantaan Virus Infection.J Virol. 2015 Dec;89(23):11834-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01610-15. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26378166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bougeret C, Mansur IG, Dastot H, et al. Increased surface expression of a newly identified 150-kDa dimer early after human T lymphocyte activation. 1992:318–323. - PubMed
-
- Spriggs MK. Shared resources between the neural and immune systems: semaphorins join the ranks. Current Opinion in Immunology. 1999;11:387–391. - PubMed
-
- Kikutani H, Kumanogoh A. Semaphorins in interactions between T cells and antigen-presenting cells. Nature reviews. 2003;3:159–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

