High-resolution imaging of the dynamic tumor cell vascular interface in transparent zebrafish
- PMID: 17954920
- PMCID: PMC2077269
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0703446104
High-resolution imaging of the dynamic tumor cell vascular interface in transparent zebrafish
Abstract
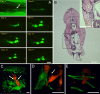
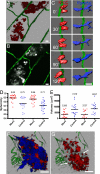
Cell metastasis is a highly dynamic process that occurs in multiple steps. Understanding this process has been limited by the inability to visualize tumor cell behavior in real time by using animal models. Here, we employ translucent zebrafish and high-resolution confocal microscopy to study how human cancer cells invade in tissues, induce angiogenesis, and interact with newly formed vessels. We use this system to study how the human metastatic gene RhoC promotes the initial steps of metastasis. We find that RhoC expression induces a primitive amoeboid-like cell invasion characterized by the formation of dynamic membrane protrusions and blebs. Surprisingly, these structures penetrate the blood vessel wall exclusively at sites of vascular remodeling and not at regions of existing intact vessels. This process requires tumor cells to secrete VEGF, which induces vascular openings, which in turn, serve as portholes allowing access of RhoC-expressing cells to the blood system. Our results support a model in which the early steps in intravasation and metastasis require two independent events: (i) dynamic regulation of the actin/myosin cytoskeleton within the tumor cell to form protrusive structures and (ii) vascular permeablization and vessel remodeling. The integration of zebrafish transgenic technology with human cancer biology may aid in the development of cancer models that target specific organs, tissues, or cell types within the tumors. Zebrafish could also provide a cost-effective means for the rapid development of therapeutic agents directed at blocking human cancer progression and tumor-induced angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gupta PB, Mani S, Yang J, Hartwell K, Weinberg RA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005;70:291–297. - PubMed
-
- Gupta G, Massaque J. Cell. 2006;127:679–695. - PubMed
-
- Condeelis J, Segall JE. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:921–930. - PubMed
-
- Zon LI, Peterson RT. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:35–44. - PubMed
-
- Berghmans S, Jette C, Langenau D, Hsu K, Stewart R, Look T, Kanki JP. BioTechniques. 2005;39:227–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

