Mediastinal pancreatic pseudocyst--a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 17955064
- PMCID: PMC1994836
Mediastinal pancreatic pseudocyst--a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
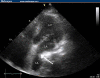
Pancreatic pseudocyst, a common complication of acute or chronic pancreatitis, in rare instances may also extend to the mediastinum. A case of 67-year-old woman presenting with a triad of chest pain, dysphagia, and dyspnea is presented. The patient had an episode of acute alcoholic pancreatitis 1 year before presentation. Chest radiography on admission showed a retrocardiac opacity. Two-dimensional echocardiography revealed an echolucent mass compressing the left atrium. A subsequent upper gastrointestinal series for her dysphagia showed extrinsic compression of the distal esophagus. Finally a definitive diagnosis was made with computed tomography (scan), which revealed a 19 x 12 cm pseudocyst extending from the body of pancreas into the thorax and compressing the esophagus and the cardiac chambers. A mediastinal pseudocyst can cause symptoms due to compression or invasion of surrounding structures. The fluid collection may enlarge slowly and hence the symptoms can be delayed as in our patient. The pseudocyst was successfully treated using endoscopic ultrasound-guided transesophageal drainage. Approximately 50 cases of mediastinal extension of the pancreatic pseudocyst in the world literature are reported. At this time, this is only the second time that successful drainage of a mediastinal pseudocyst using a transesophageal approach under endoscopic ultrasound guidance has been reported. The literature was reviewed for clinical presentation, complications, and available treatment options for mediastinal pancreatic pseudocysts.
Figures


References
-
- Sandberg AA, Dervenis C. Pancreatic pseudocysts in the 21st century. Part 1: classification, pathophysiology, anatomic considerations and treatment. JOP. 2004;5:8–24. - PubMed
-
- Vosoghi M, Sial S, Garrett B, Feng J, Lee T, Stabile BE, Eysselein VE. Medscape Gen Med. 4(3) Posted on July 18, 2002. Available at http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/Mediastinal 432491 Accessed April 3, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Vitas GJ, Sarr MG. Selected management of pancreatic pseudocyst: operative versus expectant management. Surgery. 1992;111:123–130. - PubMed
-
- Rose EA, Haider M, Yang SK. Mediastinal extension of pancreatic pseudocyst. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:3638–3639. - PubMed
-
- Mallavarapu R, Habib TH, Elton E, Goldberg MJ. Resolution of mediastinal pancreatic pseudocysts with transpapillary stent placement. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;53:367–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
