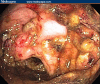
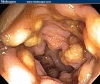
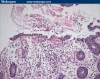
Refractory Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea
- PMID: 17955101
- PMCID: PMC1994858
Refractory Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo selection of moxifloxacin-resistant Clostridium difficile.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 May;56(5):2788-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.06433-11. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22371889 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Challenges in the diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection.Gastroenterology. 2014 Jun;146(7):1820-2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.04.013. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24768590 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In vivo selection of rifamycin-resistant Clostridium difficile during rifaximin therapy.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Nov;56(11):6019-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00974-12. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22908175 Free PMC article.
-
Future novel therapeutic agents for Clostridium difficile infection.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Jul;19(7):825-36. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2010.495386. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20521993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clostridium difficile bacteremia, Taiwan.Emerg Infect Dis. 2010 Aug;16(8):1204-10. doi: 10.3201/eid1608.100064. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20678312 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of Clostridium difficile infection: a review.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Jan;56(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1411-2. Epub 2010 Oct 6. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 20924675 Review.
References
-
- Barbut F, Corthier G, Charpak Y, et al. Prevalence and pathogenicity of Clostridium difficile in hospitalized patients: a French multicenter study. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:1449–1454. - PubMed
-
- Kyne L, Sougioultzis S, McFarland LV, Kelly CP. Underlying disease severity as a major risk factor for nosocomial Clostridium difficile diarrhea. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2002;23:653–659. - PubMed
-
- Tedesco FJ. Pseudomembranous colitis: pathogenesis and therapy. Med Clin North Am. 1982;66:655–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical