Thick slices from tomosynthesis data sets: phantom study for the evaluation of different algorithms
- PMID: 17955296
- PMCID: PMC3043718
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-007-9075-y
Thick slices from tomosynthesis data sets: phantom study for the evaluation of different algorithms
Abstract
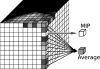
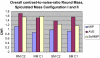
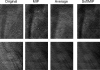
Tomosynthesis is a 3-dimensional mammography technique that generates thin slices separated one to the other by typically 1 mm from source data sets. The relatively high image noise in these thin slices raises the value of 1-cm thick slices computed from the set of reconstructed slices for image interpretation. In an initial evaluation, we investigated the potential of different algorithms for generating thick slices from tomosynthesis source data (maximum intensity projection-MIP; average algorithm-AV, and image generation by means of a new algorithm, so-called softMip). The three postprocessing techniques were evaluated using a homogeneous phantom with one textured slab with a total thickness of about 5 cm in which two 0.5-cm-thick slabs contained objects to simulate microcalcifications, spiculated masses, and round masses. The phantom was examined by tomosynthesis (GE Healthcare). Microcalcifications were simulated by inclusion of calcium particles of four different sizes. The slabs containing the inclusions were examined in two different configurations: adjacent to each other and close to the detector and with the two slabs separated by two 1-cm thick breast equivalent material slabs. The reconstructed tomosynthesis slices were postprocessed using MIP, AV, and softMip to generate 1-cm thick slices with a lower noise level. The three postprocessing algorithms were assessed by calculating the resulting contrast versus background for the simulated microcalcifications and contrast-to-noise ratios (CNR) for the other objects. The CNRs of the simulated round and spiculated masses were most favorable for the thick slices generated with the average algorithm, followed by softMip and MIP. Contrast of the simulated microcalcifications was best for MIP, followed by softMip and average projections. Our results suggest that the additional generation of thick slices may improve the visualization of objects in tomosynthesis. This improvement differs from the different algorithms for microcalcifications, speculated objects, and round masses. SoftMip is a new approach combining features of MIP and average showing image properties in between MIP and AV.
Figures





Similar articles
-
softMip: a novel projection algorithm for ultra-low-dose computed tomography.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2008 May-Jun;32(3):480-4. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0b013e31812e4b37. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2008. PMID: 18520560
-
Comparison study of reconstruction algorithms for prototype digital breast tomosynthesis using various breast phantoms.Radiol Med. 2016 Feb;121(2):81-92. doi: 10.1007/s11547-015-0583-4. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Radiol Med. 2016. PMID: 26383027
-
Breast tomosynthesis using the multiple projection algorithm adapted for stationary detectors.J Xray Sci Technol. 2016;24(1):23-41. doi: 10.3233/XST-160538. J Xray Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 26890907
-
Evaluation of back projection methods for breast tomosynthesis image reconstruction.J Digit Imaging. 2015 Jun;28(3):338-45. doi: 10.1007/s10278-014-9736-6. J Digit Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25384538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital tomosynthesis: technique.Radiol Clin North Am. 2014 May;52(3):489-97. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2014.01.003. Radiol Clin North Am. 2014. PMID: 24792651 Review.
Cited by
-
Contrast detail phantom comparison on a commercially available unit. Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM).J Digit Imaging. 2011 Feb;24(1):58-65. doi: 10.1007/s10278-009-9270-0. J Digit Imaging. 2011. PMID: 20131074 Free PMC article.
-
A review of breast tomosynthesis. Part II. Image reconstruction, processing and analysis, and advanced applications.Med Phys. 2013 Jan;40(1):014302. doi: 10.1118/1.4770281. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23298127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital mammography imaging: breast tomosynthesis and advanced applications.Radiol Clin North Am. 2010 Sep;48(5):917-29. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2010.06.009. Radiol Clin North Am. 2010. PMID: 20868894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of contrast-enhanced digital mammography and contrast-enhanced digital breast tomosynthesis for lesion assessment.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2019 Jul;6(3):031407. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.6.3.031407. Epub 2019 Feb 13. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2019. PMID: 30766895 Free PMC article.
-
Elastographic Tomosynthesis From X-Ray Strain Imaging of Breast Cancer.IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2019 Aug 19;7:4300312. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2019.2935721. eCollection 2019. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2019. PMID: 31497411 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

