Interaction of Delta sleep-inducing peptide and valproate on metaphit audiogenic seizure model in rats
- PMID: 17957464
- PMCID: PMC11517280
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-007-9222-5
Interaction of Delta sleep-inducing peptide and valproate on metaphit audiogenic seizure model in rats
Abstract
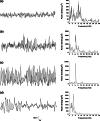
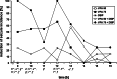
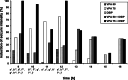
Effects of valproate (VPA), a conventional antiepileptic drug and natural delta sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP) on metaphit (1-[1-(3-isothiocyanatophenyl)-cyclohexyl]-piperidine)-induced audiogenic reflex epilepsy were studied. For the purpose of the study, valproate in the doses of 50 or 75 mg/kg and DSIP (1.0 mg/kg) was i.p. injected either alone or in combination to adult Wistar male rats with fully developed metaphit seizures after eight audiogenic testing. The animals were stimulated using an electric bell (100 +/- 3 dB and 5-8 kHz, for 60 s) 60 min after metaphit injection and afterwards at hourly intervals during the experiment. For EEG recording and power spectra analysis, three gold-plated screws were implanted into the scull. In EEGs of metaphit-treated animals polyspikes, spike-wave complexes and sleep-like patterns were recorded, while the power spectra were increased. Combined treatment of metaphit-induced seizures with valproate and DSIP was more effective than drugs alone especially during 4 h after administration. None of the applied dose combinations eliminated the EEG signs of metaphit-provoked epileptiform activity. Taken together, the results of the present study suggest that the combinations of valproate and DSIP should be considered as beneficial polytherapy in metaphit model of epilepsy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anticonvulsant, but not antiepileptic, action of valproate on audiogenic seizures in metaphit-treated rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 Oct;34(10):1010-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04681.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17714087
-
Delta sleep-inducing peptide and its tetrapeptide analogue alleviate severity of metaphit seizures.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004 Feb;77(2):227-34. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2003.10.014. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004. PMID: 14751449
-
[Delta sleep-inducing peptide and its analogues alleviate the severity of metaphit-induced audiogenic seizures in rats].Med Pregl. 2007 Sep-Oct;60(9-10):436-40. doi: 10.2298/mpns0710436s. Med Pregl. 2007. PMID: 18265587 Serbian.
-
[Behavioral and electroencephalographic effects of delta sleep inducing peptide and its analogue on metaphit-induced audiogenic seizures in rats].Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2004 Nov-Dec;132(11-12):421-6. doi: 10.2298/sarh0412421s. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2004. PMID: 15938222 Serbian.
-
[Endogenous anticonvulsants: neuropeptide Y and delta sleep inducing peptide].Med Pregl. 2008 May-Jun;61(5-6):252-5. doi: 10.2298/mpns0806252s. Med Pregl. 2008. PMID: 19102071 Review. Serbian.
Cited by
-
Two types of seizures in homocysteine thiolactone-treated adult rats, behavioral and electroencephalographic study.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009 May;29(3):329-39. doi: 10.1007/s10571-008-9324-8. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 18972205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad S, Fowler LJ, Whitton PS (2005) Effects of combined lamotrigine and valproate on basal and stimulated extra cellular amino acids and monoamines in the hippocampus of freely moving rats. Naunyn-Schmiedberg’s Arch Pharmacol 371:1–8 - PubMed
-
- Albanese R, Hogan MV, Reith M, Wieraszko A (1995) Metaphit amplifies long-term potentiation (LTP) in the mouse hippocampus. Life Sci 56:399–406 - PubMed
-
- Allen IM (1945) Observations on cases of reflex epilepsy. N Z Med J 44:135–142
-
- Bahh BE, Balosso S, Hamilton T, Herzog H, Beck-Sickinger AG, Sperk G, Gehlert DR, Vezzani A, Colmers A (2005) The anti-epileptic actions of neuropeptide Y in the hippocampus are mediated by Y2 and not Y5 receptors. Eur J Neurosci 22:1417–1430 - PubMed
-
- Baraban SC (2004) Neuropeptide Y and epilepsy: recent progress, prospects and controversies. Neuropeptides 38:261–265 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

