RKIP does not contribute to MAP kinase pathway silencing in the Merkel Cell Carcinoma cell line UISO
- PMID: 17958888
- PMCID: PMC2140056
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3163-6-16
RKIP does not contribute to MAP kinase pathway silencing in the Merkel Cell Carcinoma cell line UISO
Abstract
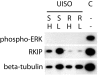
Background: The Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) has been shown to block MAP kinase pathway as well as NFkappaB signalling. By means of immunohistochemistry, we previously demonstrated that the MAP kinase pathway is virtually inactive in Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). Similarly to MCC in situ high RKIP expression accompanies absence of ERK phosphorylation in the MCC cell line UISO suggesting that RKIP might be causative for MAP kinase pathway silencing.
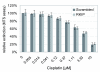
Methods: Applying an siRNA approach RKIP expression was knocked down in UISO cells and a possible influence on MAP kinase pathway activity was assessed by Western blot analysis using phospho-specific antibodies. Moreover, a possible effect of RKIP knock down in UISO cells on proliferation as well as chemosensitivity to cisplatin were examined applying the MTS assay.
Results: Surprisingly the absence of phosphorylation of the MAP kinases ERK1 and ERK 2 even following growth factor stimulation was not affected by the RKIP knock down indicating that RKIP is not essential for blocking the MAP kinase pathway in the MCC cell line UISO. Moreover, proliferation as well as chemosensitivity towards cisplatin were not altered upon knock down of RKIP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Absence of classical MAP kinase pathway signalling in Merkel cell carcinoma.J Invest Dermatol. 2006 May;126(5):1135-42. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700170. J Invest Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 16498399
-
Activation of the MAP kinase pathway induces apoptosis in the Merkel cell carcinoma cell line UISO.J Invest Dermatol. 2007 Sep;127(9):2116-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700857. Epub 2007 May 3. J Invest Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17476292
-
[Relationship between raf kinase inhibitor protein and metastasis of ovarian carcinoma].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Jul;44(7):522-8. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19957553 Chinese.
-
Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein: structure, function, regulation of cell signaling, and pivotal role in apoptosis.Adv Cancer Res. 2004;91:169-200. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(04)91005-6. Adv Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15327891 Review.
-
Regulation of the MAPK pathway by raf kinase inhibitory protein.Crit Rev Oncog. 2014;19(6):405-15. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.2014011922. Crit Rev Oncog. 2014. PMID: 25597351 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Raf-kinase inhibitor protein in colorectal cancer and its regulation by hydroxycamptothecine.J Biomed Sci. 2015 Jul 16;22(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12929-015-0162-y. J Biomed Sci. 2015. PMID: 26177829 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression by Bcr-Abl contributes to chronic myelogenous leukemia proliferation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 26;285(9):6585-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.075788. Epub 2009 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20028985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller RW, Rabkin CS. Merkel cell carcinoma and melanoma: etiological similarities and differences. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1999;8:153–158. - PubMed
-
- Houben R, Ortmann S, Schrama D, Herold MJ, Berberich I, Reichardt HM, Becker JC. Activation of the MAP Kinase Pathway Induces Apoptosis in the Merkel Cell Carcinoma Cell Line UISO. J Invest Dermatol. 2007 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

