Endometriosis-induced vaginal hyperalgesia in the rat: effect of estropause, ovariectomy, and estradiol replacement
- PMID: 17959309
- PMCID: PMC2175176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.09.022
Endometriosis-induced vaginal hyperalgesia in the rat: effect of estropause, ovariectomy, and estradiol replacement
Abstract
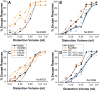
Endometriosis (ENDO) is a painful disorder defined by extrauteral endometrial growths. It is created in rats by autotransplanting pieces of uterus (which form cysts), or, for shamENDO, fat (no cysts). ENDO induces vaginal hyperalgesia, likely via central sensitization. The severity of this hyperalgesia correlates with estradiol levels during the estrous cycle, suggesting the hyperalgesia is estradiol-modulated. If so, then hyperalgesic severity should track estradiol changes during reproductive senescence (estropause) when estradiol levels initially decrease, then increase. Using psychophysical methods to assess vaginal nociception, we found that the severity of ENDO-induced hyperalgesia paralleled estradiol changes during estropause: hyperalgesia first decreased, then returned. Furthermore, the return occurred regardless of the presence of the cysts (excised in some rats). This finding provides further support for ENDO's likely centrally-mediated effects. Additionally, the results suggest that elimination of estradiol via ovariectomy (OVX) should alleviate ENDO-induced hyperalgesia and estradiol replacement should restore it. However, in healthy and shamENDO rats, OVX produces a vaginal hyperalgesia that is alleviated by estradiol, likely via estradiol's peripheral influences on the vagina. Hence, we tested the hypothesis that OVX in ENDO rats would trigger a different type of vaginal hyperalgesia dependent on the loss of estradiol. We predicted that the opposing influences of estradiol on ENDO- and OVX-induced hyperalgesia would cancel each other. As predicted, OVX had no effect on ENDO-induced hyperalgesia and estradiol replacement alleviated it. These results suggest that, in intact rats, ENDO-induced vaginal hyperalgesia is exacerbated by estradiol, and that different mechanisms underlie ENDO-induced versus OVX-induced vaginal hyperalgesia.
Figures

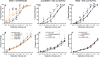
Similar articles
-
Endometriosis-induced vaginal hyperalgesia in the rat: role of the ectopic growths and their innervation.Pain. 2009 Dec 15;147(1-3):255-64. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.09.022. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Pain. 2009. PMID: 19819623 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of endometriosis on visceromotor and cardiovascular responses induced by vaginal distention in the rat.Pain. 2007 Nov;132 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S96-S103. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.04.039. Epub 2007 Jun 1. Pain. 2007. PMID: 17544211 Free PMC article.
-
Estrous changes in vaginal nociception in a rat model of endometriosis.Horm Behav. 2003 Aug;44(2):123-31. doi: 10.1016/s0018-506x(03)00121-1. Horm Behav. 2003. PMID: 13129484
-
Pain and endometriosis.Pain. 2007 Nov;132 Suppl 1:S22-S25. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.07.006. Epub 2007 Aug 29. Pain. 2007. PMID: 17761388 Review. No abstract available.
-
Endometriosis-Associated Pain - Do Preclinical Rodent Models Provide a Good Platform for Translation?Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2020;232:25-55. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-51856-1_3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 33278006 Review.
Cited by
-
Contraceptive effect and potential side-effects of deslorelin acetate implants in rats (Rattus norvegicus): preliminary observations.Can J Vet Res. 2012 Jul;76(3):209-14. Can J Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 23277700 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Identifying therapeutic candidates for endometriosis through a transcriptomics-based drug repositioning approach.iScience. 2024 Mar 2;27(4):109388. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109388. eCollection 2024 Apr 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38510116 Free PMC article.
-
Endometriosis leads to central nervous system-wide glial activation in a mouse model of endometriosis.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Mar 6;20(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02713-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36879305 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of α₂δ-1 Calcium Channel Subunit in the Spinal Cord Contributes to Pelvic Organ Cross-Sensitization in a Rat Model of Experimentally-Induced Endometriosis.Neurochem Res. 2015 Jun;40(6):1267-73. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1592-3. Epub 2015 May 3. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25935199
-
Visceral organ cross-sensitization - an integrated perspective.Auton Neurosci. 2010 Feb 16;153(1-2):106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2009.07.006. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Auton Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 19679518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bachmann GA, Nevadunsky NS. Diagnosis and treatment of atrophic vaginitis. Am Fam Physician. 2000;61:3090–6. - PubMed
-
- Becker JB, Arnold AP, Berkley KJ, Blaustein JD, Eckel LA, Hampson E, Herman JP, Marts S, Sadee W, Steiner M, Taylor J, Young E. Strategies and methods for research on sex differences in brain and behavior. Endocrinology. 2005;146:1650–73. - PubMed
-
- Berkley KJ. A life of pelvic pain. Physiol Behav. 2005;86:272–80. - PubMed
-
- Berkley KJ, Robbins A, Sato Y. Functional differences between afferent fibers in the hypogastric and pelvic nerves innervating female reproductive organs in the rat. J Neurophysiol. 1993;69:533–44. - PubMed
-
- Berkley KJ, Wood E, Scofield SL, Little M. Behavioral responses to uterine or vaginal distention in the rat. Pain. 1995;61:121–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

