Rapid onset of intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in primary human immunodeficiency virus infection is driven by an imbalance between immune response and mucosal repair and regeneration
- PMID: 17959677
- PMCID: PMC2224350
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01449-07
Rapid onset of intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in primary human immunodeficiency virus infection is driven by an imbalance between immune response and mucosal repair and regeneration
Abstract
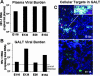
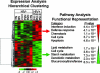
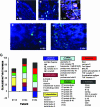
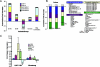
Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is an early target for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection and is a site for severe CD4(+) T-cell depletion. HIV-associated enteropathy is well-documented in chronic HIV-1 infection. However, the initial host responses to HIV infection in GALT and the early molecular correlates of HIV enteropathogenesis have not been characterized during primary HIV infection. In this study, we provide evidence of viral replication in GALT resident CD4(+) T cells and macrophages in primary-stage patients and identify early patterns of host mucosal responses and changes in the molecular microenvironment through gene expression profiling. High levels of viral replication in GALT and marked CD4(+) T-cell depletion correlated with decreased expression levels of genes regulating epithelial barrier maintenance and digestive/metabolic functions. These changes coincided with a marked increase in the transcription of immune activation-, inflammation-, and apoptosis-associated genes. Our findings indicate that HIV-induced pathogenesis in GALT emerges at both the molecular and cellular levels prior to seroconversion in primary HIV infection, potentially setting the stage for disease progression by impairing the ability to control viral replication and repair and regenerate intestinal mucosal tissues.
Figures

References
-
- Andersson, J., S. Kinloch, A. Sonnerborg, J. Nilsson, T. E. Fehniger, A. L. Spetz, H. Behbahani, L. E. Goh, H. McDade, B. Gazzard, H. Stellbrink, D. Cooper, and L. Perrin. 2002. Low levels of perforin expression in CD8+ T lymphocyte granules in lymphoid tissue during acute human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 1851355-1358. - PubMed
-
- Blattner, W. A., K. A. Oursler, F. Cleghorn, M. Charurat, A. Sill, C. Bartholomew, N. Jack, T. O'Brien, J. Edwards, G. Tomaras, K. Weinhold, and M. Greenberg. 2004. Rapid clearance of virus after acute HIV infection: correlates of risk of AIDS. J. Infect. Dis. 1891793-1801. - PubMed
-
- Brenchley, J. M., D. A. Price, and D. C. Douek. 2006. HIV disease: fallout from a mucosal catastrophe? Nat. Immunol. 7235-239. - PubMed
-
- Canani, R. B., G. De Marco, A. Passariello, V. Buccigrossi, S. Ruotolo, I. Bracale, F. Porcaro, G. Bifulco, and A. Guarino. 2006. Inhibitory effect of HIV Tat protein on the sodium-d-glucose symporter of human intestinal epithelial cells. AIDS 205-10. - PubMed
-
- Dennis, G., Jr., B. T. Sherman, D. A. Hosack, J. Yang, W. Gao, H. C. Lane, and R. A. Lempicki. 2003. DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4P3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

