Targeted synthesis of 1-(4-hydroxyiminomethylpyridinium)-3-pyridiniumpropane dibromide--a new nerve agent reactivator
- PMID: 17960099
- PMCID: PMC6149109
- DOI: 10.3390/12081964
Targeted synthesis of 1-(4-hydroxyiminomethylpyridinium)-3-pyridiniumpropane dibromide--a new nerve agent reactivator
Abstract
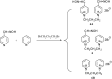
Preparation of 1-(4-hydroxy-iminomethylpyridinium)-3-pyridiniumpropane dibromide is described. This compound represents a new acetylcholinesterase (AChE) reactivator, which has no substituents on the second pyridinium ring as found in other commonly used AChE reactivators. The reactivation ability of this reactivator was tested on tabun- and cyclosarin-inhibited AChE. According to the results obtained, the new compound (without substitution and with decreased molecule size) showed increased reactivation potency in case of cyclosarin inhibited AChE. A potent oxime for treatment of tabun and cyclosarin-caused intoxications was thus obtained via slight modification of the reactivator structure (compared to trimedoxime and K027).
Figures
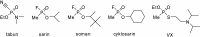
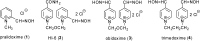
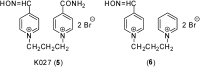
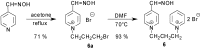
References
-
- Bajgar J. Organophosphates/nerve agent poisoning: mechanism of action, diagnosis, prophylaxis, and treatment. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2004;38:151–216. - PubMed
-
- Tu A.T. Chemical Terrorism: Horrors in Tokyo Subway and Matsumoto City. Alaken Inc.; Fort Collins, CO: 2002.
-
- Matousek J. Health and environmental threats associated with the destruction of chemical weapons. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006;1076:549–558. - PubMed
-
- Poziomek E.J., Hackley B.E., Steinberg G.M. J. Pyridinium aldoximes. J. Org. Chem. 1958;23:714–717.
-
- Lüttringhaus A., Hagedorn I. Quaternary hydroxyiminomethylpyridinium salts. The dischloride of bis-(4-hydroxyiminomethyl-1-pyridinium-methyl)-ether (Lueh6), a new reactivator of acetylcholinesterase inhibited by organic phosphoric acid esters. Arzneimittelforschung. 1964;14:1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

