Parkinson's disease: a dual-hit hypothesis
- PMID: 17961138
- PMCID: PMC7194308
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2007.00874.x
Parkinson's disease: a dual-hit hypothesis
Abstract
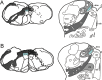
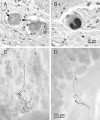
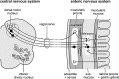
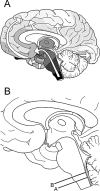
Accumulating evidence suggests that sporadic Parkinson's disease has a long prodromal period during which several non-motor features develop, in particular, impairment of olfaction, vagal dysfunction and sleep disorder. Early sites of Lewy pathology are the olfactory bulb and enteric plexus of the stomach. We propose that a neurotropic pathogen, probably viral, enters the brain via two routes: (i) nasal, with anterograde progression into the temporal lobe; and (ii) gastric, secondary to swallowing of nasal secretions in saliva. These secretions might contain a neurotropic pathogen that, after penetration of the epithelial lining, could enter axons of the Meissner's plexus and, via transsynaptic transmission, reach the preganglionic parasympathetic motor neurones of the vagus nerve. This would allow retrograde transport into the medulla and, from here, into the pons and midbrain until the substantia nigra is reached and typical aspects of disease commence. Evidence for this theory from the perspective of olfactory and autonomic dysfunction is reviewed, and the possible routes of pathogenic invasion are considered. It is concluded that the most parsimonious explanation for the initial events of sporadic Parkinson's disease is pathogenic access to the brain through the stomach and nose - hence the term 'dual-hit'.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parkinson's disease: the dual hit theory revisited.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Jul;1170:615-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04365.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19686202 Review.
-
Combination of 'idiopathic' REM sleep behaviour disorder and olfactory dysfunction as possible indicator for alpha-synucleinopathy demonstrated by dopamine transporter FP-CIT-SPECT.Brain. 2005 Jan;128(Pt 1):126-37. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh322. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Brain. 2005. PMID: 15548552
-
The nonmotor features of Parkinson's disease: pathophysiology and management advances.Curr Opin Neurol. 2016 Aug;29(4):467-73. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000348. Curr Opin Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27262147 Review.
-
Olfactory Dysfunction as an Early Biomarker in Parkinson's Disease.Neurosci Bull. 2017 Oct;33(5):515-525. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0170-x. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Neurosci Bull. 2017. PMID: 28831680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α-Synuclein BAC transgenic mice exhibit RBD-like behaviour and hyposmia: a prodromal Parkinson's disease model.Brain. 2020 Jan 1;143(1):249-265. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz380. Brain. 2020. PMID: 31816026
Cited by
-
Olfactory Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease, Its Functional and Neuroanatomical Correlates.NeuroSci. 2023 Jun 5;4(2):134-151. doi: 10.3390/neurosci4020013. eCollection 2023 Jun. NeuroSci. 2023. PMID: 39483318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association of vagal atrophy with parameters of autonomic function in multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024 Aug 21;17:17562864241267300. doi: 10.1177/17562864241267300. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024. PMID: 39175851 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's disease and gut microbiota: from clinical to mechanistic and therapeutic studies.Transl Neurodegener. 2023 Dec 15;12(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s40035-023-00392-8. Transl Neurodegener. 2023. PMID: 38098067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The microbiome of the upper respiratory tract in health and disease.BMC Biol. 2019 Nov 7;17(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0703-z. BMC Biol. 2019. PMID: 31699101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Colonic biopsies to assess the neuropathology of Parkinson's disease and its relationship with symptoms.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 14;5(9):e12728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012728. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20856865 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Hague K, Lento P, Morgello S, Caro S, Kaufmann H. The distribution of Lewy bodies in pure autonomic failure: autopsy findings and review of the literature. Acta Neuropathol 1997; 94: 92–6 - PubMed
-
- Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S. Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol 1999; 56: 33–9 - PubMed
-
- Jellinger KA. Neuropathological spectrum of synucleinopathies. Mov Disord 2003; 18 (Suppl. 6): 2–12 - PubMed
-
- Litvan I, Bhatia KP, Burn DJ, Goetz CG, Lang AE, McKeith I. SIC Task force appraisal of clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinsonian disorders. Mov Disord 2003; 18: 467–86 - PubMed
-
- Geser F, Wenning GK, Poewe W, McKeith I. How to diagnose dementia with Lewy bodies: state of the art. Mov Disord 2005; 20 (Suppl. 12): 11–20 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

