Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) regulates Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) expression in microglia
- PMID: 17961202
- PMCID: PMC2423670
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04838.x
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) regulates Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) expression in microglia
Abstract
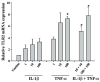
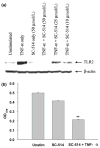
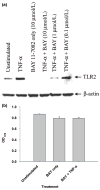
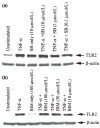
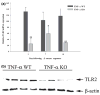
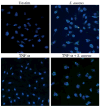
Microglia represent one effector arm of CNS innate immunity as evident by their role in pathogen recognition. We previously reported that exposure of microglia to Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), a prevalent CNS pathogen, led to elevated Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) expression, a pattern recognition receptor capable of recognizing conserved structural motifs associated with gram-positive bacteria such as S. aureus. In this study, we demonstrate that the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) enhances TLR2 expression in microglia, whereas interleukin-1beta has no significant effect. To determine the downstream signaling events responsible for elevated microglial TLR2 expression in response to TNF-alpha, a series of signal transduction inhibitors were employed. Treatment with caffeic acid phenethyl ester, an inhibitor of redox-mediated nuclear factor-kappa B activation, significantly attenuated TNF-alpha-induced TLR2 expression. Similar results were observed with the IKK-2 and IkappaB-alpha inhibitors SC-514 and BAY 11-7082, respectively. In contrast, no significant alterations in TLR2 expression were observed with protein kinase C or p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors. A definitive role for TNF-alpha was demonstrated by the inability of S. aureus to augment TLR2 expression in microglia isolated from TNF-alpha knockout mice. In addition, TLR2 expression was significantly attenuated in brain abscesses of TNF-alpha knockout mice. Collectively, these results indicate that in response to S. aureus, TNF-alpha acts in an autocrine/paracrine manner to enhance TLR2 expression in microglia and that this effect is mediated, in part, by activation of the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TLR2 expression in astrocytes is induced by TNF-alpha- and NF-kappa B-dependent pathways.J Immunol. 2008 Sep 15;181(6):3841-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.6.3841. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18768838 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidoglycan enhances proinflammatory cytokine expression through the TLR2 receptor, MyD88, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT and NF-kappaB pathways in BV-2 microglia.Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Aug;10(8):883-91. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.04.026. Epub 2010 May 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20451669
-
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2)-TLR9 crosstalk dictates IL-12 family cytokine production in microglia.Glia. 2012 Jan;60(1):29-42. doi: 10.1002/glia.21243. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Glia. 2012. PMID: 21901759 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Toll-like receptor 1 and 2 agonist Pam3CSK4 on uveal melanocytes and relevant experimental mouse model.Exp Eye Res. 2024 Feb;239:109749. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2023.109749. Epub 2023 Dec 17. Exp Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38113956 Review.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediated signaling in neuronal homeostasis and dysfunction.Cell Signal. 2010 Jul;22(7):977-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.01.010. Epub 2010 Jan 21. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20096353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parthenolide Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats by Reducing Inflammation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jan 6;2023:8759766. doi: 10.1155/2023/8759766. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 36644442 Free PMC article.
-
Theiler's virus infection induces TLR3-dependent upregulation of TLR2 critical for proinflammatory cytokine production.Glia. 2009 Aug 15;57(11):1216-26. doi: 10.1002/glia.20843. Glia. 2009. PMID: 19191335 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and spatial heterogeneity of microglia in Rasmussen encephalitis.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Nov 21;10(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01472-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 36411471 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences and effects of estrogenic compounds on the expression of inflammatory molecules by astrocytes exposed to the insecticide dimethoate.Neurotox Res. 2014 Apr;25(3):271-85. doi: 10.1007/s12640-013-9417-0. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Neurotox Res. 2014. PMID: 23943137
-
Exacerbation of diabetes due to F. Nucleatum LPS-induced SGLT2 overexpression in the renal proximal tubular epithelial cells.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jan 24;26(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-03965-z. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39856606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal BB. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:745–756. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Aloisi F. Immune function of microglia. Glia. 2001;36:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC, Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD, Baldwin AS. A nucleosomal function for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Nature. 2003;423:659–663. - PubMed
-
- Beg AA, Baltimore D. An essential role for NF-kappaB in preventing TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Science. 1996;274:782–784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

