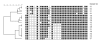Characterisation of mycobacteria isolated from slaughter cattle in pastoral regions of Uganda
- PMID: 17961243
- PMCID: PMC2140064
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-95
Characterisation of mycobacteria isolated from slaughter cattle in pastoral regions of Uganda
Abstract
Background: Bovine tuberculosis is a zoonotic problem in pastoral cattle and communities in Uganda. Tuberculin tests in pastoral cattle had shown a high herd but low animal prevalence, with a high proportion of avian reactors. No work had been done to identify the mycobacterial species involved. The objective of the study was to isolate and characterise Mycobacterial species causing tuberculous lesions in slaughtered animals. Lesioned organs compatible with bovine tuberculosis in slaughtered cattle from pastoral areas in Uganda were collected and cultured to isolate mycobacteria. AccuProbe culture identification kits for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, M. avium complex and M. avium were used to identify the isolates. Spoligotyping and Insertion Sequence (IS) 1311 and IS1245 Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism analysis (RFLP) were used to further characterise the isolates.
Results: Of the 61 lesioned organs and tissues cultured, 19 isolates were identified as M. bovis, 3 as M. avium subsp.hominissuis, 1 as M. intracellulare, 1 as a mixed culture of M. bovis and M. avium sp. and 1 as M. avium sp. and unidentified mycobacteria. Eleven other mycobacteria outside the tuberculosis and avium complex groups were also isolated. Ten new spoligopatterns grouped into three clusters were identified from M. bovis isolates. Two of the three M. avium subsp.hominissuis isolates showed similar patterns on the IS1311 RFLP but all were different on the IS1245 RFLP.
Conclusion: The isolation of M. bovis confirms the ongoing infection with spoligotypes unique to Uganda. Isolation of environmental mycobacteria could explain the high avian or non specific tuberculin reactor patterns commonly observed in pastoral cattle and suggests their pathogenic or opportunistic role in the infection of cattle with disseminated bovine tuberculous lesions.
Figures
References
-
- Acen F. Msc Thesis Monograph. Makerere University; 1991. Pre and Post-slaughter diagnosis of tuberculosis in cattle in Kampla abattoir-Uganda.
-
- WHO/FAO/OIE . Report on Consultation on Animal Tuberculosis Vaccines. WHO. Geneva: Veterinary Public Health Unit; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources