Protein kinase inhibitors reduce GABA but not glutamate release in the nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 17961609
- PMCID: PMC2196408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.09.004
Protein kinase inhibitors reduce GABA but not glutamate release in the nucleus accumbens
Abstract
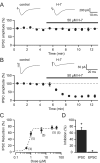
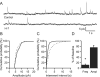
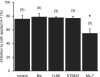
We investigated the role of endogenous protein kinase activity on synaptic transmission in the rat nucleus accumbens slice. The isoquinolinesulfonamide H-7 (50muM), a non-selective serine/threonine protein kinase inhibitor, had no effect on pharmacologically isolated glutamatergic EPSCs. However, it reduced GABA release in a dose-dependent manner. This effect of H-7 was not mimicked by the selective cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor H-89, the PKC inhibitor Bisindolylmaleimide-1, or the cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor KT5823. However, bath application of the myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) inhibitor, ML-7, significantly reduced IPSC amplitudes and partially occluded the reduction in IPSCs observed following bath application of H-7. These results suggest that endogenous protein kinase activity, specifically MLCK activity, regulates GABA, but not glutamate release, onto medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of nitric oxide, cyclic GMP and phosphodiesterase 5 in excitatory amino acid and GABA release in the nucleus accumbens evoked by activation of the hippocampal fimbria.Neuroscience. 2002;112(2):331-43. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00079-9. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 12044451
-
Group II metabotropic glutamate receptor modulation of excitatory transmission in rat subthalamic nucleus.J Physiol. 2003 Dec 1;553(Pt 2):489-96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.052209. Epub 2003 Sep 18. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14500768 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine excites nucleus accumbens neurons through the differential modulation of glutamate and GABA release.J Neurosci. 2004 Sep 29;24(39):8621-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3280-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15456835 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission in the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus.Brain Res. 2010 Apr 14;1325:28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.02.021. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20153735
-
GABA(B) restrains release from singly-evoked GABA terminals.Neuroscience. 2011 Oct 13;193:54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.042. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21820490 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PKA-RIIβ autophosphorylation modulates PKA activity and seizure phenotypes in mice.Commun Biol. 2021 Mar 1;4(1):263. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01748-4. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33649504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldwin AE, Sadeghian K, Holahan MR, Kelley AE. Appetitive instrumental learning is impaired by inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase within the nucleus accumbens. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2002;77:44–62. - PubMed
-
- Carroll RC, Nicoll RA, Malenka RC. Effects of PKA and PKC on miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in CA1 pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1998;80:2797–2800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

