Parenting very low birth weight children at school age: maternal stress and coping
- PMID: 17961686
- PMCID: PMC10228568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.04.012
Parenting very low birth weight children at school age: maternal stress and coping
Abstract
Objective: To compare severity and determinants of stress and coping in mothers of 8-year-old very low birth weight (VLBW) and term children varying in medical and developmental risk.
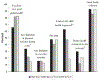
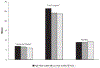
Study design: Three groups of mothers/infants were prospectively compared in a longitudinal study from birth to 8 years (110 high-risk VLBW, 80 low-risk VLBW, and 112 term). Maternal psychological distress, coping, parenting/marital stress, child health, and family impact were measured in the children at age 8 years.
Results: Mothers of VLBW children differed from term mothers, reporting less consensus with partners, more concern for their children's health, less parent-child conflict, and fewer years of education attained. Mothers of high-risk VLBW children experienced the greatest family and personal strains and used less denial and disengagement coping. The groups exhibited no differences in the sense of parenting competence, divorce rate, parenting/marital satisfaction, family cohesion, and psychological distress symptoms. Multiple birth, low socioeconomic status, and lower child IQ added to maternal stress.
Conclusions: VLBW birth has long-term negative and positive impacts on maternal/family outcomes related to the infant's medical risk.
Figures
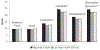
Comment in
-
Parenting stress and childhood impairment.J Pediatr. 2007 Nov;151(5):448-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.08.020. J Pediatr. 2007. PMID: 17961683 No abstract available.
References
-
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Sutton PD, Ventura SJ, Menacker F, Munson ML. Births: final data for 2003. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2005;54:1–116. - PubMed
-
- Bhutta AT, Cleves MA, Casey PH, Cradock MM, Anand KJ. Cognitive and behavioral outcomes of school-aged children who were born preterm: a meta-analysis. JAMA 2002;288:728–77. - PubMed
-
- Saigal S, Rosenbaum PL, Feeny D, Burrows E, Furlong W, Stoskoph BL, et al. Parental perspectives of the health status and health-related quality of life of teenage children who were extremely low birth weight and term controls. Pediatr 2000;105:569–74. - PubMed
-
- Culver G, Fallor K, Londner RB. Informed decisions for extremely low birth-weight infants. JAMA 2000;283:3201–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

