Folic acid-mediated targeting of cowpea mosaic virus particles to tumor cells
- PMID: 17961827
- PMCID: PMC2293326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2007.08.015
Folic acid-mediated targeting of cowpea mosaic virus particles to tumor cells
Abstract
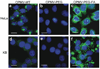
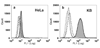
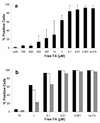
Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV) is a well-characterized nanoparticle that has been used for a variety of nanobiotechnology applications. CPMV interacts with several mammalian cell lines and tissues in vivo. To overcome natural CPMV targeting and redirect CPMV particles to cells of interest, we attached a folic acid-PEG conjugate by using the copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction. PEGylation of CPMV completely eliminated background binding of the virus to tumor cells. The PEG-folate moiety allowed CPMV-specific recognition of tumor cells bearing the folate receptor. In addition, by testing CPMV formulations with different amounts of the PEG-FA moiety displayed on the surface, we show that higher-density loading of targeting ligands on CPMV may not be necessary for efficient targeting to tumor cells. These studies help to define the requirements for efficiently targeting nanoparticles and protein cages to tumors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PEGylated viral nanoparticles for biomedicine: the impact of PEG chain length on VNP cell interactions in vitro and ex vivo.Biomacromolecules. 2009 Apr 13;10(4):784-92. doi: 10.1021/bm8012742. Biomacromolecules. 2009. PMID: 19281149 Free PMC article.
-
Guiding plant virus particles to integrin-displaying cells.Nanoscale. 2012 Jun 21;4(12):3698-705. doi: 10.1039/c2nr30571b. Epub 2012 May 15. Nanoscale. 2012. PMID: 22585108 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV) nanoparticles with antigen presenting cells in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 23;4(11):e7981. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007981. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19956734 Free PMC article.
-
Cowpea mosaic virus nanoparticles for cancer imaging and therapy.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019 May;145:130-144. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019. PMID: 31004625 Review.
-
Structure-based engineering of an icosahedral virus for nanomedicine and nanotechnology.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;327:23-58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-69379-6_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19198569 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular targeted viral nanoparticles as tools for imaging cancer.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1108:211-30. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-751-8_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24243252 Free PMC article.
-
Using viruses as nanomedicines.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;171(17):4001-9. doi: 10.1111/bph.12662. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24571489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein cage nanoparticles bearing the LyP-1 peptide for enhanced imaging of macrophage-rich vascular lesions.ACS Nano. 2011 Apr 26;5(4):2493-502. doi: 10.1021/nn102863y. Epub 2011 Mar 21. ACS Nano. 2011. PMID: 21391720 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-like particles: Next-generation nanoparticles for targeted therapeutic delivery.Bioeng Transl Med. 2017 Jan 19;2(1):43-57. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10049. eCollection 2017 Mar. Bioeng Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29313023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-assembly in the ferritin nano-cage protein superfamily.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(8):5406-21. doi: 10.3390/ijms12085406. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21954367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jaracz S, Chen J, Kuznetsova LV, Ojima I. Recent advances in tumor-targeting anticancer drug conjugates. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005;13:5043–5054. - PubMed
-
- Lee RJ, L PS. Delivery of Liposomes into Cultured KB cells via Folate Receptor-mediated endocytosis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994;269:3198–3204. - PubMed
-
- Sonvico F, Mornet S, Vasseur S, Dubernet C, Jaillard D, Degrouard J, Hoebeke J, Duguet E, Colombo P, Couvreur P. Folate-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles for solid tumor targeting as potential specific magnetic hyperthermia mediators: synthesis, physicochemical characterization, and in vitro experiments. Bioconjug Chem. 2005;16:1181–1188. - PubMed
-
- Choi Y, B JRJ. Targeting cancer cells with DNA-assembled dendrimers: a mix and match strategy for cancer. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:669–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

