Development and preclinical evaluation of an alphavirus replicon vaccine for influenza
- PMID: 17961878
- PMCID: PMC2706696
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.09.038
Development and preclinical evaluation of an alphavirus replicon vaccine for influenza
Abstract
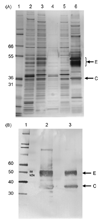
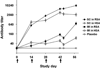
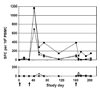
We used a propagation-defective, single-cycle, alphavirus replicon vector system to produce virus-like replicon particles (VRP) expressing the hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) proteins from influenza A/Wyoming/03/2003 (H3N2). Efficient production methods were scaled to produce pilot lots of HA VRP and NA VRP and clinical lots of HA VRP. HA VRP-induced high-titered antibody responses in mice, rabbits and rhesus macaques, as measured by ELISA or hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assays, and robust cellular immune responses in mice and rhesus macaques, as measured by IFN-gamma ELISPOT. NA VRP also induced cellular immune responses in mice. A toxicology study with HA VRP and NA VRP in rabbits showed no adverse effects in any parameter. These studies support clinical testing of alphavirus replicon vaccines for influenza.
Figures


References
-
- Treanor JJ. Influenza virus. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. fifth ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2000. pp. 1823–1849.
-
- Thomas DB, Patera AC, Graham CM, Smith CA. Antibody-mediated immunity. In: Nicholson KG, Webster RG, Hay AJ, editors. Textbook of Influenza. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd; 1998. pp. 267–277.
-
- Beutner KR, Chow T, Rubi E, Strussenberg J, Clement J, Ogra PL. Evaluation of a neuraminidase-specific influenza A virus vaccine in children: antibody responses and effects on two successive outbreaks of natural infection. J Infect Dis. 1979;140(Dec 6):844–850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

