Robotic partial nephrectomy for complex renal tumors: surgical technique
- PMID: 17961910
- PMCID: PMC2644902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.09.047
Robotic partial nephrectomy for complex renal tumors: surgical technique
Abstract
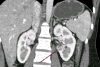
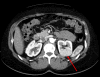
Objectives: Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy requires advanced training to accomplish tumor resection and renal reconstruction while minimizing warm ischemia times. Complex renal tumors add an additional challenge to a minimally invasive approach to nephron-sparing surgery. We describe our technique, illustrated with video, of robotic partial nephrectomy for complex renal tumors, including hilar, endophytic, and multiple tumors.
Methods: Robotic assistance was used to resect 14 tumors in eight patients (mean age: 50.3 yr; range: 30-68 yr). Three patients had hereditary kidney cancer. All patients had complex tumor features, including hilar tumors (n=5), endophytic tumors (n=4), and/or multiple tumors (n=3).
Results: Robotic partial nephrectomy procedures were performed successfully without complications. Hilar clamping was used with a mean warm ischemia time of 31 min (range: 24-45 min). Mean blood loss was 230 ml (range: 100-450 ml). Histopathology confirmed clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (n=3), hybrid oncocytic tumor (n=2), chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (n=2), and oncocytoma (n=1). All patients had negative surgical margins. Mean index tumor size was 3.6 cm (range: 2.6-6.4 cm). Mean hospital stay was 2.6 d. At 3-mo follow-up, no patients experienced a statistically significant change in serum creatinine or estimated glomerular filtration rate and there was no evidence of tumor recurrence.
Conclusions: Robotic partial nephrectomy is safe and feasible for select patients with complex renal tumors, including hilar, endophytic, and multiple tumors. Robotic assistance may facilitate a minimally invasive, nephron-sparing approach for select patients with complex renal tumors who might otherwise require open surgery or total nephrectomy.
Figures




Comment in
-
Editorial comment on: Robotic partial nephrectomy for complex renal tumors: surgical technique.Eur Urol. 2008 Mar;53(3):522-3. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.09.049. Epub 2007 Oct 15. Eur Urol. 2008. PMID: 17961908 No abstract available.
-
Editorial comment on: Robotic partial nephrectomy for complex renal tumors: surgical technique.Eur Urol. 2008 Mar;53(3):521-2. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.09.048. Epub 2007 Oct 15. Eur Urol. 2008. PMID: 17961911 No abstract available.
References
-
- Allaf ME, Bhayani SB, Rogers C, Varkarakis I, Link RE, Inagaki T, Jarrett TW, Kavoussi LR. Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: evaluation of long-term oncological outcome. J Urol. 2004;172:871–873. - PubMed
-
- Lane BR, Gill IS. 5-Year outcomes of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy. J Urol. 2007;177:70–74. - PubMed
-
- Patel V. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty. Urol. 2005;66:45–49. - PubMed
-
- Klingler DW, Hemstreet GP, Balaji KC. Feasibility of robotic radical nephrectomy--initial results of single-institution pilot study. Urol. 2005;65:1086–1089. - PubMed
-
- Horgan S, Benedetti E, Moser F. Robotically assisted donor nephrectomy for kidney transplantation. Am J Surg. 2004;188:45S–51S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

