Histone deactylase 1 expression is increased in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia subjects: analysis of the National Brain Databank microarray collection
- PMID: 17961987
- PMCID: PMC2254186
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2007.09.020
Histone deactylase 1 expression is increased in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia subjects: analysis of the National Brain Databank microarray collection
Abstract
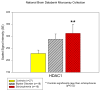
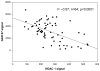
Histone deactylase enzymes are responsible for the deacetylation of histone tails, and consequently influence gene regulation through their ability to modify chromatin structure surrounding promoter regions. We analyzed the microarray collection of the National Brain Databank to investigate differential expression of these enzymes in the prefrontal cortices of control, schizophrenia and bipolar subjects. HDAC1 expression levels were significantly higher in schizophrenia versus normal subjects. The mRNA expression level of an epigenetically regulated schizophrenia candidate gene GAD67 was strongly and negatively correlated with the mRNA expression levels of HDAC1, HDAC3 and HDAC4 levels. These findings provide additional support for the proposal that epigenetic factors are operative in the brain pathology of patients with schizophrenia.
Figures
References
-
- Abdolmaleky HM, Cheng KH, Russo A, Smith CL, Faraone SV, Wilcox M, Shafa R, Glatt SJ, Nguyen G, Ponte JF, Thiagalingam S, Tsuang MT. Hypermethylation of the reelin (RELN) promoter in the brain of schizophrenic patients: a preliminary report. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005;134(1):60–6. - PubMed
-
- Abdolmaleky HM, Cheng KH, Faraone SV, Wilcox M, Glatt SJ, Gao F, Smith CL, Shafa R, Aeali B, Carnevale J, Pan H, Papageorgis P, Ponte JF, Sivaraman V, Tsuang MT, Thiagalingam S. Hypomethylation of MB-COMT promoter is a major risk factor for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(21):3132–45. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akbarian S, Ruehl MG, Bliven E, Luiz LA, Peranelli AC, Baker SP, Roberts RC, Bunney WE, Jr, Conley RC, Jones EG, Tamminga CA, Guo Y. Chromatin alterations associated with down-regulated metabolic gene expression in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(8):829–40. - PubMed
-
- Akbarian S, Huang HS. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of altered GAD1/GAD67 expression in schizophrenia and related disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2006;52(2):293–304. - PubMed
-
- Alarcon JM, Malleret G, Touzani K, Vronskaya S, Ishii S, Kandel ER, Barco A. Chromatin acetylation, memory, and LTP are impaired in CBP+/− mice: a model for the cognitive deficit in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome and its amelioration. Neuron. 2004;42(6):947–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

