Differential regulation of native estrogen receptor-regulatory elements by estradiol, tamoxifen, and raloxifene
- PMID: 17962382
- PMCID: PMC2234590
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2007-0340
Differential regulation of native estrogen receptor-regulatory elements by estradiol, tamoxifen, and raloxifene
Abstract
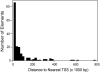
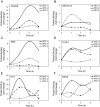
Estrogen receptors (ERs) regulate gene transcription by interacting with regulatory elements. Most information regarding how ER activates genes has come from studies using a small set of target genes or simple consensus sequences such as estrogen response element, activator protein 1, and Sp1 elements. However, these elements cannot explain the differences in gene regulation patterns and clinical effects observed with estradiol (E(2)) and selective estrogen receptor modulators. To obtain a greater understanding of how E(2) and selective estrogen receptor modulators differentially regulate genes, it is necessary to investigate their action on a more comprehensive set of native regulatory elements derived from ER target genes. Here we used chromatin immunoprecipitation-cloning and sequencing to isolate 173 regulatory elements associated with ERalpha. Most elements were found in the introns (38%) and regions greater than 10 kb upstream of the transcription initiation site (38%); 24% of the elements were found in the proximal promoter region (<10 kb). Only 11% of the elements contained a classical estrogen response element; 23% of the elements did not have any known response elements, including one derived from the naked cuticle homolog gene, which was associated with the recruitment of p160 coactivators. Transfection studies found that 80% of the 173 elements were regulated by E(2), raloxifene, or tamoxifen with ERalpha or ERbeta. Tamoxifen was more effective than raloxifene at activating the elements with ERalpha, whereas raloxifene was superior with ERbeta. Our findings demonstrate that E(2), tamoxifen, and raloxifene differentially regulate native ER-regulatory elements isolated by chromatin immunoprecipitation with ERalpha and ERbeta.
Figures


References
-
- Writing Group for the Women’s Health Initiative 2002 Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: principal results From the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA 288:321–333 - PubMed
-
- MacGregor JI, Jordan VC 1998 Basic guide to the mechanisms of antiestrogen action. Pharmacol Rev 50:151–196 - PubMed
-
- Jordan VC 2004 Selective estrogen receptor modulation: concept and consequences in cancer. Cancer Cell 5:207–213 - PubMed
-
- Cummings S, Eckert S, Krueger K, Grady D, Powles T, Cauley J, Norton L, Nickelsen T, Bjarnason N, Morrow M, Lippman ME, Black D, Glusman J, Costa A, Jordan V 1999 The effect of raloxifene on risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. JAMA [Erratum (1999) 282:2184] 281:2189–2197 - PubMed
-
- Ettinger B, Black D, Mitlak B, Knickerbocker R, Nickelsen T, Genant H, Christiansen C, Delmas P 1999 Reduction of vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated with raloxifene. Results from a 3-year randomized clinical trial. JAMA 282:637–644 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

