A cell cycle regulatory network controlling NF-kappaB subunit activity and function
- PMID: 17962807
- PMCID: PMC2099464
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601899
A cell cycle regulatory network controlling NF-kappaB subunit activity and function
Retraction in
-
Retraction: 'A cell cycle regulatory network controlling NF-κB subunit activity and function'.EMBO J. 2014 Sep 1;33(17):1978. doi: 10.15252/embj.201470010. Epub 2014 Jul 28. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 25069773 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
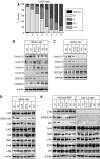
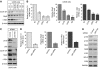
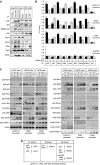
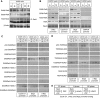
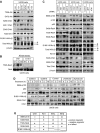
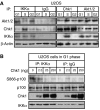
Aberrantly active NF-kappaB complexes can contribute to tumorigenesis by regulating genes that promote the growth and survival of cancer cells. We have investigated NF-kappaB during the cell cycle and find that its ability to regulate the G1-phase expression of key proto-oncogenes is subject to regulation by the integrated activity of IkappaB kinase (IKK)alpha, IKKbeta, Akt and Chk1. The coordinated binding of NF-kappaB subunits to the Cyclin D1, c-Myc and Skp2 promoters is dynamic with distinct changes in promoter occupancy and RelA(p65) phosphorylation occurring through G1, S and G2 phases, concomitant with a switch from coactivator to corepressor recruitment. Akt activity is required for IKK-dependent phosphorylation of NF-kappaB subunits in G1 and G2 phases, where Chk1 is inactive. However, in S-phase, Akt is inactivated, while Chk1 phosphorylates RelA and associates with IKKalpha, inhibiting the processing of the p100 (NF-kappaB2) subunit, which also plays a critical role in the regulation of these genes. These data reveal a complex regulatory network integrating NF-kappaB with the DNA-replication checkpoint and the expression of critical regulators of cell proliferation.
Figures




References
-
- Albanese C, D'Amico M, Reutens AT, Fu M, Watanabe G, Lee RJ, Kitsis RN, Henglein B, Avantaggiati M, Somasundaram K, Thimmapaya B, Pestell RG (1999) Activation of the cyclin D1 gene by the E1A-associated protein p300 through AP-1 inhibits cellular apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274: 34186–34195 - PubMed
-
- Bromberg JF, Fan Z, Brown C, Mendelsohn J, Darnell JE Jr (1998) Epidermal growth factor-induced growth inhibition requires Stat1 activation. Cell Growth Differ 9: 505–512 - PubMed
-
- Campbell KJ, Rocha S, Perkins ND (2004) Active repression of antiapoptotic gene expression by RelA(p65) NF-κB. Mol Cell 13: 853–865 - PubMed
-
- Campbell KJ, Witty JM, Rocha S, Perkins ND (2006) Cisplatin mimics ARF tumor suppressor regulation of RelA (p65) nuclear factor-κB transactivation. Cancer Res 66: 929–935 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

