Extensive ssDNA end formation at DNA double-strand breaks in non-homologous end-joining deficient cells during the S phase
- PMID: 17963495
- PMCID: PMC2174948
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-97
Extensive ssDNA end formation at DNA double-strand breaks in non-homologous end-joining deficient cells during the S phase
Abstract
Background: Efficient and correct repair of DNA damage, especially DNA double-strand breaks, is critical for cellular survival. Defects in the DNA repair may lead to cell death or genomic instability and development of cancer. Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) is the major repair pathway for DNA double-strand breaks in mammalian cells. The ability of other repair pathways, such as homologous recombination, to compensate for loss of NHEJ and the ways in which contributions of different pathways are regulated are far from fully understood.
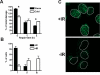
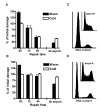
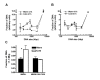
Results: In this report we demonstrate that long single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) ends are formed at radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in NHEJ deficient cells. At repair times > or = 1 h, processing of unrejoined DNA double-strand breaks generated extensive ssDNA at the DNA ends in cells lacking the NHEJ protein complexes DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) or DNA Ligase IV/XRCC4. The ssDNA formation was cell cycle dependent, since no ssDNA ends were observed in G1-synchronized NHEJ deficient cells. Furthermore, in wild type cells irradiated in the presence of DNA-PKcs (catalytic subunit of DNA-PK) inhibitors, or in DNA-PKcs deficient cells complemented with DNA-PKcs mutated in six autophosphorylation sites (ABCDE), no ssDNA was formed. The ssDNA generation also greatly influences DNA double-strand break quantification by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, resulting in overestimation of the DNA double-strand break repair capability in NHEJ deficient cells when standard protocols for preparing naked DNA (i. e., lysis at 50 degrees C) are used.
Conclusion: We provide evidence that DNA Ligase IV/XRCC4 recruitment by DNA-PK to DNA double-strand breaks prevents the formation of long ssDNA ends at double-strand breaks during the S phase, indicating that NHEJ components may downregulate an alternative repair process where ssDNA ends are required.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of DNA double strand break repair and chromosome aberration formation.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;104(1-4):14-20. doi: 10.1159/000077461. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15162010 Review.
-
The role of nonhomologous DNA end joining, conservative homologous recombination, and single-strand annealing in the cell cycle-dependent repair of DNA double-strand breaks induced by H(2)O(2) in mammalian cells.Radiat Res. 2008 Dec;170(6):784-93. doi: 10.1667/RR1375.1. Radiat Res. 2008. PMID: 19138034
-
Biochemical evidence for Ku-independent backup pathways of NHEJ.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Sep 15;31(18):5377-88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg728. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12954774 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-induced genomic rearrangements formed by nonhomologous end-joining of DNA double-strand breaks.Cancer Res. 2001 May 15;61(10):3886-93. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11358801
-
[Double strand break repair, one mechanism can hide another: alternative non-homologous end joining].Cancer Radiother. 2012 Feb;16(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2011.05.004. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Cancer Radiother. 2012. PMID: 21737335 Review. French.
Cited by
-
DNA double-strand-break complexity levels and their possible contributions to the probability for error-prone processing and repair pathway choice.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Sep;41(16):7589-605. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt556. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23804754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dianhydrogalactitol synergizes with topoisomerase poisons to overcome DNA repair activity in tumor cells.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 24;11(7):577. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02780-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32709853 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Filamin A as a BRCA1-interacting protein required for efficient DNA repair.Cell Cycle. 2010 Apr 1;9(7):1421-33. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.7.11256. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20305393 Free PMC article.
-
A noncatalytic function of the ligation complex during nonhomologous end joining.J Cell Biol. 2013 Jan 21;200(2):173-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201203128. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23337116 Free PMC article.
-
The Genomes of Three Uneven Siblings: Footprints of the Lifestyles of Three Trichoderma Species.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Feb 10;80(1):205-327. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00040-15. Print 2016 Mar. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26864432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hefferin ML, Tomkinson AE. Mechanism of DNA double-strand break repair by non-homologous end joining. DNA Repair (Amst) 2005;4:639–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

