Interactions of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder therapeutic agents with the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein
- PMID: 17963743
- PMCID: PMC2659508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.09.035
Interactions of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder therapeutic agents with the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein
Abstract
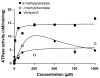
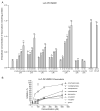
The objective of this study was to assess the potential interactions of the drug transporter P-glycoprotein with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) therapeutic agents atomoxetine--and the individual isomers of methylphenidate, amphetamine, and modafinil utilizing established in vitro assay. An initial ATPase assay indicated that both d- and l-methylphenidate have weak affinity for P-glycoprotein. The intracellular accumulation of P-glycoprotein substrates doxorubicin and rhodamine123 in the P-glycoprotein overexpressing cell line LLC-PK1/MDR1 was determined to evaluate potential inhibitory effects on P-glycoprotein. The results demonstrated that all compounds, except both modafinil isomers, significantly increased doxorubicin and rhodamine123 accumulation in LLC-PK1/MDR1 cells at higher concentrations. To investigate the P-glycoprotein substrate properties, the intracellular concentrations of the tested compounds in LLC-PK1/MDR1 and P-glycoprotein negative LLC-PK1 cells were measured in the presence and absence of the P-glycoprotein inhibitor PSC833. The results indicate that the accumulation of d-methylphenidate in LLC-PK1 cells was 32.0% higher than in LLC-PK1/MDR1 cells. Additionally, coadministration of PSC833 leads to 52.9% and 45.6% increases in d-modafinil and l-modafinil accumulation, respectively, in LLC-PK1/MDR1 cells. Further studies demonstrated that l-modafinil transport across LLC-PK1/MDR1 cell monolayers in the basolateral-to-apical (B-A) direction was significantly higher than in the apical-to-basolateral (A-B) direction. PSC833 treatment significantly decreased the transport of l-modafinil in B-A direction. In conclusion, our results suggest that all tested agents with the exception of modafinil isomers are relatively weak P-glycoprotein inhibitors. Furthermore, P-glycoprotein may play a minor role in the transport of d-methylphenidate, d-modafinil, and l-modafinil.
Figures


References
-
- Angrist B, Corwin J, Bartlik B, Cooper T. Early pharmacokinetics and clinical effects of oral D-amphetamine in normal subjects. Biol Psychiatry. 1987;22:1357–1368. - PubMed
-
- Beringer PM, Slaughter RL. Transporters and their impact on drug disposition. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39:1097–1108. - PubMed
-
- Bertelsen KM, Greenblatt DJ, von Moltke LL. Apparent active transport of MDMA is not mediated by P-glycoprotein: a comparison with MDCK and Caco-2 monolayers. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2006;27:219–227. - PubMed
-
- Bosch TM, Meijerman I, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH. Genetic polymorphisms of drug-metabolising enzymes and drug transporters in the chemotherapeutic treatment of cancer. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006;45:253–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

