Attenuation of AMPA receptor activity improves motor skills in a mouse model of juvenile Batten disease
- PMID: 17963751
- PMCID: PMC4418195
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.09.012
Attenuation of AMPA receptor activity improves motor skills in a mouse model of juvenile Batten disease
Abstract
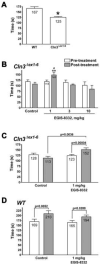
Juvenile Batten disease, caused by mutations in the CLN3 gene, is a fatal, incurable neurodegenerative disorder in children. The Cln3-loss-of-function (Cln3(Deltaex1-6)) mouse model of the disease exhibits many characteristic pathological features of the human disorder including a deficit in motor skills. Our recent findings [Kovács, A.D., Weimer, J.M., Pearce, D.A., 2006. Selectively increased sensitivity of cerebellar granule cells to AMPA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in a mouse model of Batten disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 22, 575-585] suggested that the neurological deficit in the Cln3(Deltaex1-6) mouse model of the disease might result from an abnormally increased AMPA receptor activity in the cerebellum. Therefore, we tested if administration of low doses of an AMPA receptor antagonist, that attenuate AMPA receptor function but avoid a toxic, complete blockade of the receptor, have beneficial effects in Cln3(Deltaex1-6) mice. Here we show that attenuation of AMPA receptor activity by a single intraperitoneal injection of the non-competitive AMPA antagonist, EGIS-8332 (1 mg/kg), significantly improves the motor skills of Cln3(Deltaex1-6) mice. Our results provide a new, promising therapeutic approach for juvenile Batten disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age-dependent therapeutic effect of memantine in a mouse model of juvenile Batten disease.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Oct;63(5):769-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.05.040. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22683643 Free PMC article.
-
Temporary inhibition of AMPA receptors induces a prolonged improvement of motor performance in a mouse model of juvenile Batten disease.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Feb-Mar;60(2-3):405-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.10.010. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 20971125 Free PMC article.
-
Moving towards therapies for juvenile Batten disease?Exp Neurol. 2008 Jun;211(2):329-31. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.02.016. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18400221 Review.
-
Selectively increased sensitivity of cerebellar granule cells to AMPA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in a mouse model of Batten disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2006 Jun;22(3):575-85. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.12.018. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Neurobiol Dis. 2006. PMID: 16483786
-
Current Insights in Elucidation of Possible Molecular Mechanisms of the Juvenile Form of Batten Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 29;21(21):8055. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218055. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33137890 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Finding the most appropriate mouse model of juvenile CLN3 (Batten) disease for therapeutic studies: the importance of genetic background and gender.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Apr;8(4):351-61. doi: 10.1242/dmm.018804. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 26035843 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical Mouse Models of Neurodegenerative Lysosomal Storage Diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Apr 15;7:57. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00057. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32351971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De-palmitoylation by N-(tert-Butyl) hydroxylamine inhibits AMPAR-mediated synaptic transmission via affecting receptor distribution in postsynaptic densities.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Feb;25(2):187-199. doi: 10.1111/cns.12996. Epub 2018 Jun 17. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 29911316 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-mediated epilepsies.Epilepsia. 2011 May;52 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):5-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03029.x. Epilepsia. 2011. PMID: 21542839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in the Development of Small Molecule Therapeutics for the Treatment of Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinoses (NCLs).J Med Chem. 2016 May 26;59(10):4415-27. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01020. Epub 2015 Nov 24. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26565590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bialer M, Johannessen SI, Kupferberg HJ, Levy RH, Perucca E, Tomson T. Progress report on new antiepileptic drugs: a summary of the Eigth Eilat Conference (EILAT VIII). Epilepsy Res. 2007;73:1–52. - PubMed
-
- Gigler G, Móricz K, Ágoston M, Simó A, Albert M, Benedek A, Kapus G, Kertész S, Végh M, Barkóczy J, Markó B, Szabó G, Matucz E, Gacsályi I, Lévay G, Hársing LG, Jr., Szénási G. Neuroprotective and anticonvulsant effects of EGIS-8332, a non-competitive AMPA receptor antagonist, in a range of animal models. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007;152:151–160. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goebel HH. The neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses. J. Child. Neurol. 1995;10:424–437. - PubMed
-
- Gressens P, Spedding M, Gigler G, Kertész S, Villa P, Medja F, Williamson T, Kapus G, Lévay G, Szénási G, Barkóczy J, Hársing LG., Jr. The effects of AMPA receptor antagonists in models of stroke and neurodegeneration. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005;519:58–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

