Effect of phenobarbital on hepatic cell proliferation and apoptosis in mice deficient in the p50 subunit of NF-kappaB
- PMID: 17963809
- PMCID: PMC2344135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.09.019
Effect of phenobarbital on hepatic cell proliferation and apoptosis in mice deficient in the p50 subunit of NF-kappaB
Abstract
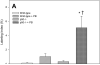
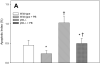
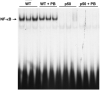
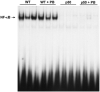
Phenobarbital (PB) is a nongenotoxic tumor promoter in the liver. One mechanism by which PB may exert its tumor promoting activity is by inducing oxidative stress. We previously found that PB administration increased hepatic NF-kappaB DNA binding activity. In this study we examined the hypothesis that the effects of PB on cell proliferation and apoptosis are dependent on NF-kappaB. We used a mouse model that is deficient in the p50 subunit of NF-kappaB; previous studies had found that p50-/- mice were less sensitive to the induction of hepatic cell proliferation by PCBs or peroxisome proliferators. Mice (p50-/- and wild-type B6129) were fed a control diet or one containing 0.05% PB for 3, 10 or 34 days. At the end of the experiment, the mice were euthanized and livers removed and processed. PB increased cell proliferation at 3 and 10 days (but not at 34 days), but the deletion of the NF-kappaB p50 subunit did not inhibit these increases. p50-/- Mice had higher cell proliferation at the 3 day (only in mice fed PB) and 34-day timepoints. PB decreased hepatocyte apoptosis after 3 days, slightly decreased it after 10 days, and did not affect it after 34 days. The deletion of the NF-kappaB p50 subunit did not influence PB's effect on apoptosis. In p50-/- mice, apoptosis was increased after 3 or 10 days compared to wild-type mice, but no effect was seen after 34 days. The hepatic expression of the NF-kappaB-regulated gene TNF-alpha correlated more with the hepatic cell proliferation data than with hepatic apoptosis, and was not decreased by the deletion of the p50 subunit. These findings show that the p50 subunit of NF-kappaB is not required for the alteration of hepatocyte proliferation or apoptosis by PB up to 34 days after its administration.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Effect of vitamin E on hepatic cell proliferation and apoptosis in mice deficient in the p50 subunit of NF-κB after treatment with phenobarbital.Food Chem Toxicol. 2011 Oct;49(10):2706-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.06.059. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Food Chem Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21726593 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of hepatocarcinogenesis by the deletion of the p50 subunit of NF-kappaB in mice administered the peroxisome proliferator Wy-14,643.Toxicol Sci. 2006 Apr;90(2):331-6. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfj116. Epub 2006 Jan 24. Toxicol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16434500
-
Effect of 2,2',4,4',5,5'-hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB-153) on hepatocyte proliferation and apoptosis in mice deficient in the p50 subunit of the transcription factor NF-kappaB.Toxicol Sci. 2004 Sep;81(1):35-42. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfh193. Epub 2004 Jun 16. Toxicol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15201435
-
Inhibition of the promotion of hepatocarcinogenesis by 2,2',4,4',5,5'-hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB-153) by the deletion of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B in mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008 Oct 15;232(2):302-8. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.06.013. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18644402 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the p50 subunit of NF-kappaB in vitamin E-induced changes in mice treated with the peroxisome proliferator, ciprofibrate.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Jun;46(6):2062-73. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.01.047. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18336980 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inactivation of NF-kappaB p50 leads to insulin sensitization in liver through post-translational inhibition of p70S6K.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 3;284(27):18368-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007260. Epub 2009 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19433583 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of vitamin E on hepatic cell proliferation and apoptosis in mice deficient in the p50 subunit of NF-κB after treatment with phenobarbital.Food Chem Toxicol. 2011 Oct;49(10):2706-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.06.059. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Food Chem Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21726593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barkett M, Gilmore TD. Control of apoptosis by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene. 1999;18:6910–6924. - PubMed
-
- Brawn MK, Chiou WJ, Leach KL. Oxidant-induced activation of protein kinase C in UC11MG cells. Free Radic Res. 1995;22:23–37. - PubMed
-
- Butler WH, Hempsall V. Histochemical observations on nodules induced in the mouse liver by phenobarbitone. J Pathol. 1978;125:155–161. - PubMed
-
- Butterworth BE, Conolly RB, Morgan KT. A strategy for establishing mode of action of chemical carcinogens as a guide for approaches to risk assessments. Cancer Lett. 1995;93:129–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

