Kainate receptors are primarily postsynaptic to SP-containing axon terminals in the trigeminal dorsal horn
- PMID: 17964552
- PMCID: PMC2238683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.09.070
Kainate receptors are primarily postsynaptic to SP-containing axon terminals in the trigeminal dorsal horn
Abstract
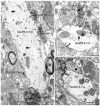
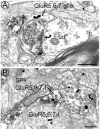
Kainate receptors (KARs) are involved in the modulation and transmission of nociceptive information from peripheral afferents to neurons in the spinal cord and trigeminal dorsal horns. KARs are found at both pre- and postsynaptic sites in the dorsal horn. We hypothesized that KARs and Substance P (SP), a modulatory neuropeptide that is used as a marker of nociceptive afferents, have a complex interactive relationship. To determine the cellular relationship and connectivity between KARs and SP afferents, we used electron microscopic dual immunocytochemical analysis to examine the ultrastructural localization of KAR subunits GluR5, 6 and 7 (GluR5,6,7) in relation to SP within laminae I and II in the rat trigeminal dorsal horn. KARs were distributed both postsynaptically in dendrites and somata (51% of GluR5,6,7 immunoreactive (-ir) profiles) and presynaptically in axons and axon terminals (45%). We also found GluR5,6,7-ir glial profiles (5%). The majority of SP-ir profiles were presynaptic axons and axon terminals. SP-ir dendritic profiles were rare, yet 23% contained GluR5,6,7 immunoreactivity. GluR5,6,7 and SP were also colocalized at presynaptic sites (18% of GluR5,6,7-ir axons and axon terminals contained SP; while 11% of SP-ir axons and axon terminals contained GluR5,6,7). The most common interaction between KARs and SP we observed was GluR5,6,7-ir dendrites contacted by SP-ir axon terminals; 54% of the dendritic targets of SP-ir axon terminals were GluR5,6,7-ir. These results provide anatomical evidence that KARs primarily mediate nociceptive transmission postsynaptic to SP-containing afferents and may also modulate the presynaptic release of SP and glutamate in trigeminal dorsal horn.
Figures

References
-
- Advokat C, Rutherford D. Selective antinociceptive effect of excitatory amino acid antagonists in intact and acute spinal rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1995;51:855–860. - PubMed
-
- Afrah AW, Fiska A, Gjerstad J, Gustafsson H, Tjolsen A, Olgart L, Stiller CO, Hole K, Brodin E. Spinal substance P release in vivo during the induction of long-term potentiation in dorsal horn neurons. Pain. 2002;96:49–55. - PubMed
-
- Aicher SA, Mitchell JL, Swanson KC, Zadina JE. Endomorphin-2 axon terminals contact mu-opioid receptor-containing dendrites in trigeminal dorsal horn. Brain Res. 2003;977:190–198. - PubMed
-
- Aicher SA, Sharma S, Cheng PY, Liu-Chen LY, Pickel VM. Dual ultrastructural localization of mu-opiate receptors and substance p in the dorsal horn. Synapse. 2000b;36:12–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

