Iron oxide nanoparticles as a drug delivery vehicle for MRI monitored magnetic targeting of brain tumors
- PMID: 17964647
- PMCID: PMC2761681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.08.050
Iron oxide nanoparticles as a drug delivery vehicle for MRI monitored magnetic targeting of brain tumors
Abstract
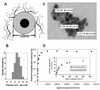
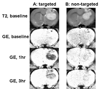
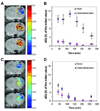
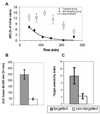
This study explored the possibility of utilizing iron oxide nanoparticles as a drug delivery vehicle for minimally invasive, MRI-monitored magnetic targeting of brain tumors. In vitro determined hydrodynamic diameter of approximately 100 nm, saturation magnetization of 94 emicro/g Fe and T2 relaxivity of 43 s(-1)mm(-)(1) of the nanoparticles suggested their applicability for this purpose. In vivo effect of magnetic targeting on the extent and selectivity of nanoparticle accumulation in tumors of rats harboring orthotopic 9L-gliosarcomas was quantified with MRI. Animals were intravenously injected with nanoparticles (12 mg Fe/kg) under a magnetic field density of 0 T (control) or 0.4 T (experimental) applied for 30 min. MR images were acquired prior to administration of nanoparticles and immediately after magnetic targeting at 1h intervals for 4h. Image analysis revealed that magnetic targeting induced a 5-fold increase in the total glioma exposure to magnetic nanoparticles over non-targeted tumors (p=0.005) and a 3.6-fold enhancement in the target selectivity index of nanoparticle accumulation in glioma over the normal brain (p=0.025). In conclusion, accumulation of iron oxide nanoparticles in gliosarcomas can be significantly enhanced by magnetic targeting and successfully quantified by MR imaging. Hence, these nanoparticles appear to be a promising vehicle for glioma-targeted drug delivery.
Figures
References
-
- Fisher PG, Buffler PA. Malignant Gliomas in 2005: Where to GO From Here? JAMA. 2005;293(5):615–617. - PubMed
-
- Newton HB. Primary brain tumors: review of etiology, diagnosis and treatment. American Family Physician. 1994;49(4):787–797. - PubMed
-
- Zhou R, Mazurchuk R, Straubinger RM. Antivasculature effects of doxorubicin-containing liposomes in an intracranial rat brain tumor model. Cancer Res. 2002;62(9):2561–2566. - PubMed
-
- Gutman RL, Peacock G, Lu DR. Targeted drug delivery for brain cancer treatment. Journal of Controlled Release. 2000;65:31–41. - PubMed
-
- Motl S, Zhuang Y, Waters CM, Stewart CF. Pharmacokinetic considerations in the treatment of CNS tumours. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006;45(9):871–903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

