The GID1-mediated gibberellin perception mechanism is conserved in the Lycophyte Selaginella moellendorffii but not in the Bryophyte Physcomitrella patens
- PMID: 17965273
- PMCID: PMC2174699
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.107.051524
The GID1-mediated gibberellin perception mechanism is conserved in the Lycophyte Selaginella moellendorffii but not in the Bryophyte Physcomitrella patens
Abstract
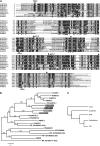
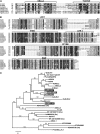
In rice (Oryza sativa) and Arabidopsis thaliana, gibberellin (GA) signaling is mediated by GIBBERELLIN-INSENSITIVE DWARF1 (GID1) and DELLA proteins in collaboration with a GA-specific F-box protein. To explore when plants evolved the ability to perceive GA by the GID1/DELLA pathway, we examined these GA signaling components in the lycophyte Selaginella moellendorffii and the bryophyte Physcomitrella patens. An in silico search identified several homologs of GID1, DELLA, and GID2, a GA-specific F-box protein in rice, in both species. Sm GID1a and Sm GID1b, GID1 proteins from S. moellendorffii, showed GA binding activity in vitro and interacted with DELLA proteins from S. moellendorffii in a GA-dependent manner in yeast. Introduction of constitutively expressed Sm GID1a, Sm G1D1b, and Sm GID2a transgenes rescued the dwarf phenotype of rice gid1 and gid2 mutants. Furthermore, treatment with GA(4), a major GA in S. moellendorffii, caused downregulation of Sm GID1b, Sm GA20 oxidase, and Sm GA3 oxidase and degradation of the Sm DELLA1 protein. These results demonstrate that the homologs of GID1, DELLA, and GID2 work in a similar manner in S. moellendorffii and in flowering plants. Biochemical studies revealed that Sm GID1s have different GA binding properties from GID1s in flowering plants. No evidence was found for the functional conservation of these genes in P. patens, indicating that GID1/DELLA-mediated GA signaling, if present, differs from that in vascular plants. Our results suggest that GID1/DELLA-mediated GA signaling appeared after the divergence of vascular plants from the moss lineage.
Figures









References
-
- Adachi, J., and Hasegawa, M. (1996). MOLPHY version 2.3: Programs for molecular phylogenetics based on maximum likelihood. Comput. Sci. Monogr. 28 1–150.
-
- Ashton, N.W., and Cove, D.J. (1977). The isolation and preliminary characterisation of auxotrophic and analogue resistant mutants in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Mol. Gen. Genet. 154 87–95.
-
- Banks, J.A. (1999). Gametophyte development in ferns. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 50 163–186. - PubMed
-
- Bolle, C. (2004). The role of GRAS proteins in plant signal transduction and development. Planta 218 683–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

