'Role reversal' for the receptor PAR1 in sepsis-induced vascular damage
- PMID: 17965715
- PMCID: PMC3059149
- DOI: 10.1038/ni1525
'Role reversal' for the receptor PAR1 in sepsis-induced vascular damage
Abstract
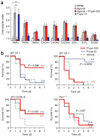
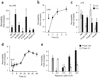
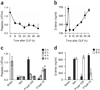
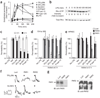
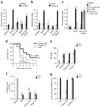
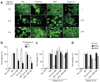
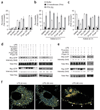
Sepsis is a deadly disease characterized by considerable derangement of the proinflammatory, anti-inflammatory and coagulation responses. Protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1), an important regulator of endothelial barrier function and blood coagulation, has been proposed to be involved in the lethal sequelae of sepsis, but it is unknown whether activation of PAR1 is beneficial or harmful. Using a cell-penetrating peptide (pepducin) approach, we provide evidence that PAR1 switched from being a vascular-disruptive receptor to a vascular-protective receptor during the progression of sepsis in mice. Unexpectedly, we found that the protective effects of PAR1 required transactivation of PAR2 signaling pathways. Our results suggest therapeutics that selectively activate PAR1-PAR2 complexes may be beneficial in the treatment of sepsis.
Figures
References
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:138–150. - PubMed
-
- Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA. Novel strategies for the treatment of sepsis. Nat. Med. 2003;9:517–524. - PubMed
-
- Parrillo JE. Pathogenetic mechanisms of septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993;328:1471–1477. - PubMed
-
- Kaneider NC, Agarwal A, Leger AJ, Kuliopulos A. Reversing systemic inflammatory response syndrome with chemokine receptor pepducins. Nat. Med. 2005;11:661–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

