A critical developmental switch defines the kinetics of kidney cyst formation after loss of Pkd1
- PMID: 17965720
- PMCID: PMC2302790
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1675
A critical developmental switch defines the kinetics of kidney cyst formation after loss of Pkd1
Abstract
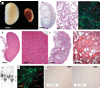
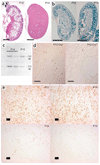
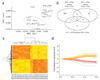
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is an important cause of end-stage renal disease, for which there is no proven therapy. Mutations in PKD1 (the gene encoding polycystin-1) are the principal cause of this disease. The disease begins in utero and is slowly progressive, but it is not known whether cystogenesis is an ongoing process during adult life. We now show that inactivation of Pkd1 in mice before postnatal day 13 results in severely cystic kidneys within 3 weeks, whereas inactivation at day 14 and later results in cysts only after 5 months. We found that cellular proliferation was not appreciably higher in cystic specimens than in age-matched controls, but the abrupt change in response to Pkd1 inactivation corresponded to a previously unrecognized brake point during renal growth and significant changes in gene expression. These findings suggest that the effects of Pkd1 inactivation are defined by a developmental switch that signals the end of the terminal renal maturation process. Our studies show that Pkd1 regulates tubular morphology in both developing and adult kidney, but the pathologic consequences of inactivation are defined by the organ's developmental status. These results have important implications for clinical understanding of the disease and therapeutic approaches.
Figures
Comment in
-
Sensitive cilia set up the kidney.Nat Med. 2007 Dec;13(12):1409-11. doi: 10.1038/nm1207-1409. Nat Med. 2007. PMID: 18064029 No abstract available.
References
-
- Boucher C, Sandford R. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD, MIM 173900, PKD1 and PKD2 genes, protein products known as polycystin-1 and polycystin-2) Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2004;12:347–354. - PubMed
-
- Pretorius DH, et al. Diagnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in utero and in the young infant. J. Ultrasound Med. 1987;6:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Piontek KB, et al. A functional floxed allele of Pkd1 that can be conditionally inactivated in vivo. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004;15:3035–3043. - PubMed
-
- Lu W, et al. Perinatal lethality with kidney and pancreas defects in mice with a targetted Pkd1 mutation. Nat. Genet. 1997;17:179–181. - PubMed
-
- Bukanov NO, Smith LA, Klinger KW, Ledbetter SR, Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O. Long-lasting arrest of murine polycystic kidney disease with CDK inhibitor roscovitine. Nature. 2006;444:949–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

