Human CtIP promotes DNA end resection
- PMID: 17965729
- PMCID: PMC2409435
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06337
Human CtIP promotes DNA end resection
Abstract
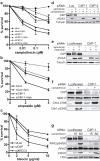
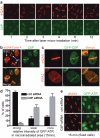
In the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle, DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are processed into single-stranded DNA, triggering ATR-dependent checkpoint signalling and DSB repair by homologous recombination. Previous work has implicated the MRE11 complex in such DSB-processing events. Here, we show that the human CtIP (RBBP8) protein confers resistance to DSB-inducing agents and is recruited to DSBs exclusively in the S and G2 cell-cycle phases. Moreover, we reveal that CtIP is required for DSB resection, and thereby for recruitment of replication protein A (RPA) and the protein kinase ATR to DSBs, and for the ensuing ATR activation. Furthermore, we establish that CtIP physically and functionally interacts with the MRE11 complex, and that both CtIP and MRE11 are required for efficient homologous recombination. Finally, we reveal that CtIP has sequence homology with Sae2, which is involved in MRE11-dependent DSB processing in yeast. These findings establish evolutionarily conserved roles for CtIP-like proteins in controlling DSB resection, checkpoint signalling and homologous recombination.
Figures



References
-
- Wyman C, Kanaar R. DNA double-strand break repair: all’s well that ends well. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2006;40:363–383. - PubMed
-
- Lieber MR, Ma Y, Pannicke U, Schwarz K. Mechanism and regulation of human non-homologous DNA end-joining. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:712–720. - PubMed
-
- West SC. Molecular views of recombination proteins and their control. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:435–445. - PubMed
-
- Sung P, Klein H. Mechanism of homologous recombination: mediators and helicases take on regulatory functions. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:739–750. - PubMed
-
- Zou L, Elledge SJ. Sensing DNA damage through ATRIP recognition of RPA-ssDNA complexes. Science. 2003;300:1542–1548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

