Electromechanical characterization of cinnamophilin, a natural thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist with anti-arrhythmic activity, in guinea-pig heart
- PMID: 17965733
- PMCID: PMC2199384
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707541
Electromechanical characterization of cinnamophilin, a natural thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist with anti-arrhythmic activity, in guinea-pig heart
Abstract
Background and purpose: Cinnamophilin, a thromboxane A(2) receptor antagonist, has been identified as a prominent anti-arrhythmic agent in rat heart. This study aimed to determine its electromechanical and anti-arrhythmic effects in guinea-pig hearts.
Experimental approach: Microelectrodes were used to study action potentials in ventricular papillary muscles. Fluo-3 fluorimetric ratio and whole-cell voltage-clamp techniques were used to record calcium transients and membrane currents in single ventricular myocytes, respectively. Intracardiac electrocardiograms were obtained and the anti-arrhythmic efficacy was determined from isolated perfused hearts.
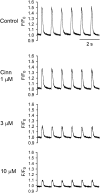
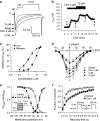
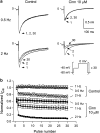
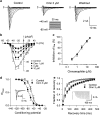
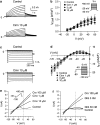
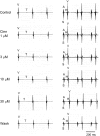
Key results: In papillary muscles, cinnamophilin decreased the maximal rate of upstroke (V(max)) and duration of action potential, and reduced the contractile force. In single ventricular myocytes, cinnamophilin reduced Ca(2+) transient amplitude. Cinnamophilin decreased the L-type Ca(2+) current (I(Ca,L))(IC(50)=7.5 microM) with use-dependency, induced a negative shift of the voltage-dependent inactivation and retarded recovery from inactivation. Cinnamophilin also decreased the Na(+) current (I(Na)) (IC(50)=2.7 microM) and to a lesser extent, the delayed outward (I(K)), inward rectifier (I(K1)), and ATP-sensitive (I(K,ATP)) K(+) currents. In isolated perfused hearts, cinnamophilin prolonged the AV nodal conduction interval and Wenckebach cycle length and the refractory periods of the AV node, His-Purkinje system and ventricle, while shortening the ventricular repolarization time. Additionally, cinnamophilin reduced the occurrence of reperfusion-induced ventricular fibrillation.
Conclusions and implications: These results suggest that the promising anti-arrhythmic effect and the changes in the electromechanical function induced by cinnamophilin in guinea-pig heart can be chiefly accounted for by inhibition of I(Ca,L) and I(Na).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multiple cellular electrophysiological effects of a novel antiarrhythmic furoquinoline derivative HA-7 [N-benzyl-7-methoxy-2,3,4,9-tetrahydrofuro[2,3-b]quinoline-3,4-dione] in guinea pig cardiac preparations.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Jan;316(1):380-91. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.092106. Epub 2005 Sep 20. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. PMID: 16174797
-
Electrophysiological and mechanical effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester, a novel cardioprotective agent with antiarrhythmic activity, in guinea-pig heart.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Feb 28;702(1-3):194-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.01.040. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23396228
-
Ionic mechanisms for the antiarrhythmic action of cinnamophilin in rat heart.J Biomed Sci. 1999 Nov-Dec;6(6):376-86. doi: 10.1007/BF02253669. J Biomed Sci. 1999. PMID: 10545773
-
Cardiac electrophysiologic and antiarrhythmic actions of a pavine alkaloid derivative, O-methyl-neocaryachine, in rat heart.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jun;136(3):459-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704736. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12023949 Free PMC article.
-
KB130015, a new amiodarone derivative with multiple effects on cardiac ion channels.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003 Fall;21(3):216-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2003.tb00117.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003. PMID: 12931255 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cardiac Arrhythmias.Cells. 2023 Feb 21;12(5):679. doi: 10.3390/cells12050679. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899814 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bernauer W. Concerning the effect of the K+ channel blocking agent glibenclamide on ischaemic and reperfusion arrhythmias. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997;326:147–156. - PubMed
-
- Billman GE. Role of ATP sensitive potassium channel in extracellular potassium accumulation and cardiac arrhythmias during myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovasc Res. 1994;28:762–769. - PubMed
-
- Chang GJ, Su MJ, Kuo SC, Lin TP, Lee YS. Multiple cellular electrophysiological effects of a novel antiarrhythmic furoquinoline derivative HA-7 [N-benzyl-7-methoxy-2,3,4,9-tetrahydrofuro[2,3-b]quinoline-3,4-dione] in guinea pig cardiac preparations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:380–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

